LIMITS, CONTINUITY AND DIFFERENTIABILITY
LIMIT OF A FUNCTION
FORMAL DEFINITION OF LIMITS
The limit of the function f(x) at x = a will be l if for every ∈>0, but small, we may find δ > 0,
such that 0 < |x – a| < δ ⇒ |f(x) – l | <∈
Symbolically, we write 
The definition given above may be stated "as the limit of the function f(x) at x = a will be l if the numerical difference between the values of f(x) and l can be made as small as we please (i.e. approaches to zero), as x approaches a (i.e. the difference of the values of x and a is sufficiently small)".
Students must be clear that at this stage we never use the above definition for the evaluation of limits.
VALUE AND LIMIT OF A FUNCTION
The value of the function f(x) at a point a, i.e. f(a), and the limiting value of the function f(x) as x approaches a, i.e., may be same or may differ. Even, we may come across some functions, which are not defined at a, i.e., a does not belong to their domain but limit can be found out at x = a. On the other hand for some functions f(a) may exist but  may not exist.
may not exist.
UNIQUENESS OF LIMIT
If 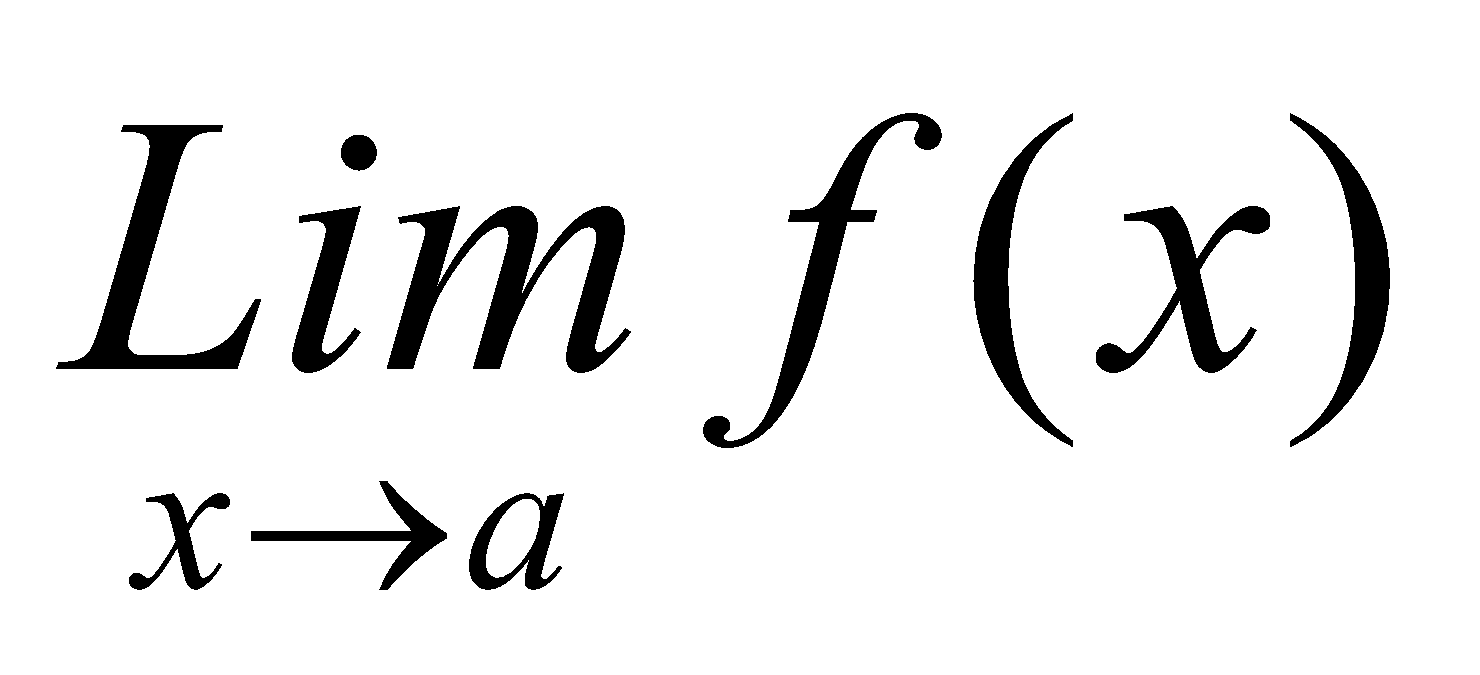 exists, it is unique. There cannot be two distinct numbers l1 and l2 such that when x tends to a, the function f(x) tends to both l1 and 12.
exists, it is unique. There cannot be two distinct numbers l1 and l2 such that when x tends to a, the function f(x) tends to both l1 and 12.
FUNDAMENTAL THEOREMS ON LIMITS
If f(x) and g(x) be two functions of x such that  and
and  both exist, then
both exist, then
where k is a fixed real number.
if exists
if exists
provided
METHODS OF EVALUATING LIMITS
DETERMINATE FORMS
LIMITS BY DIRECT SUBSTITUTION
To find , we substitute x = a in the function. If the value comes out to be a determinate value, it is the limit. That is,
, we substitute x = a in the function. If the value comes out to be a determinate value, it is the limit. That is,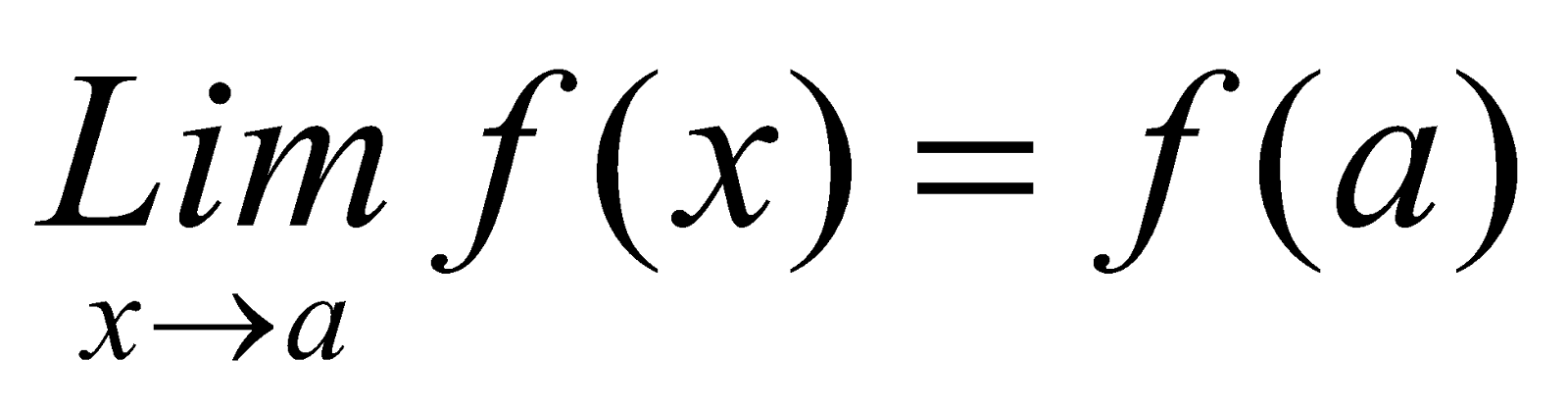 provided it exists.
provided it exists.
For example,
INDETERMINATE FORMS
If direct substitution of x = a while evaluating  leads to one of the following :
leads to one of the following :
Then it is called indeterminate form. We apply special techniques, which are discussed in the next sections :
USE OF L’ HOSPITAL RULE
If takes the form
takes the form  then
then 
Note :
- If
form then we may repeat the process.
- If the form comes out to be any other indeterminate form, it should be converted to
[see the examples].
- This method makes the evaluation of a limit very easy and may always be used in case of objective type questions. However, if the detail solution is required to be presented (for subjective type problems), L’ Hospital rule must not be used.
- L’Hospital rule is applicable only if the function f(x) and g(x) fulfil certain conditions , which are not given above as such they are not required for the problems we commonly encounter.
- Use L’Hospital rule after learning the differentiation properly.
USE OF STANDARD FORMULAE
1. Algebraic Limits
Remark : Limit in (c) in general right hand limits (i.e for x > 0)
2. Trigonometric Limits
, x in radian
, x in radian
3. Exponential Limits
4. Logarithmic Limits
LIMITS BY FACTORISATION
If  form, then x – a must be a factor of numerator and denominator which can be cancelled out.
form, then x – a must be a factor of numerator and denominator which can be cancelled out.
For example :
It is
LIMITS BY SUBSTITUTION
In order to evaluate  we may, substitute x = a + h or a – h, so that as x → a, h → 0
we may, substitute x = a + h or a – h, so that as x → a, h → 0
Thus 
This method is applied to bring the limit at zero as the most of the formulae are given as
For example : 
Put x – 10 = h, ∴ as x 10 , h
10 , h 0
0
∴ The limit is 
LIMITS OF FUNCTIONS AS X ∞
∞
is of the form
and f(x) and g(x) are both polynomials of x.
We divide numerator and denominator by the highest power of x and put 0 for
For example,
=  [After rationalisation]
[After rationalisation]
[Dividing numerator and denominator by x]
For example,
LIMITS USING EXPANSION
Many limits can be evaluated very easily by applying expansion series. Some of the standard expansions are
- (1+x)n = 1 +nC1x + nC2x2 + .......+ nCnxn,
For example,
AN IMPORTANT FORMULA FOR EVALUATING LIMITS OF 1∞ FORMS
For example,
[Applying L’Hospital rule we may use series for sin x also]
SANDWICH THEOREM
Let f , g, h be three functions such that f ≤ g ≤ h in an open interval containing a. Suppose that  exist and both are equal to l. Then
exist and both are equal to l. Then  also exists and is equal to the same l.
also exists and is equal to the same l.
For example
holds for all x
Also
- Let it is given that
Then 
EXISTENCE OF LIMIT
Consider a function f(x), whose limit as x approaches a is being evaluated. When we state that x is approaching a then x is never equal to a. Rather x is either somewhat less than a and we say that x approaches a from left, or x is somewhat greater than a and we say that x approaches a from right.
These two tendencies can be represented on the real number line as shown below.
x approaches a from left x approaches a from right
or x∈(a – δ, a), δ > 0 or x∈(a, a + δ), δ > 0
LEFT HAND LIMIT AND RIGHT HAND LIMIT
- When x tends towards a from the left (i.e. the values of x always remaining somewhat less than a), the value towards which f(x) tends is called the LEFT HAND LIMIT of f(x) at x = a. Symbolically, we write
- When x tends towards a from the right (i.e. the values of x always remaining somewhat greater than a), the value towards which f(x) tends is called the RIGHT HAND LIMIT of f(x) at x = a. Symbolically, we write
CONDITION FOR EXISTENCE OF LIMIT
- If the left hand limit (LHL) and the the right hand limit (RHL) exist at a point and are equal then we conclude that the limit of the function exists at that point.
If . Then
. Then 
- If LHL and RHL at a point exist but are not equal, then we conclude that the limit of the function does not exist at that point.
If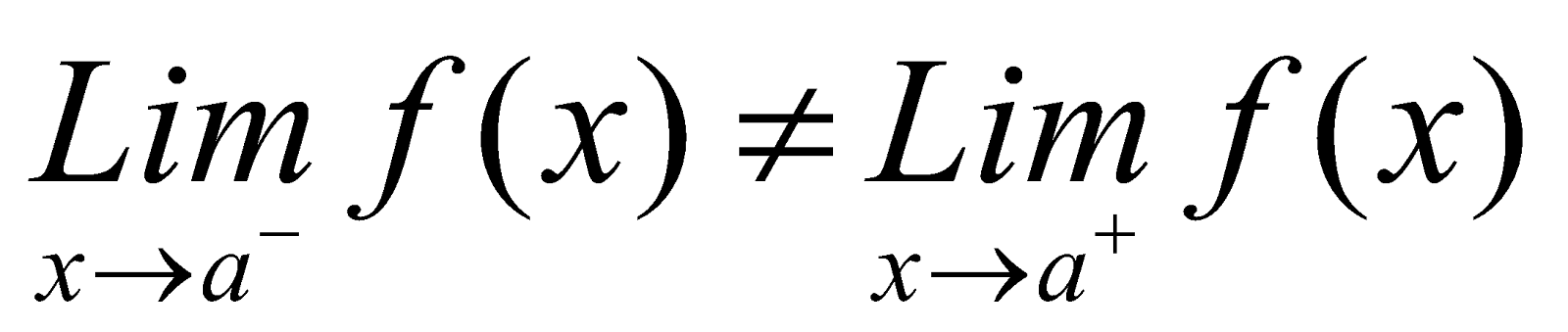 . Then
. Then  does not exist.
does not exist.
- In many functions LHL or RHL or both may not exist. For example
has neither LHL or RHL at x = 0, because as x approaches 0, f(x) does not approach to any definite value. Actually any interval containing 0, contains infinite cycles.
EVALUATION OF LHL AND RHL
Thus, to find left hand limit at x = a, we replace x by a – h in the function and evaluate the limit at h = 0
Thus, to find right hand limit at x = a, we replace x by a + h in the function and evaluate the limit at h = 0.
For example : Let f(x) = [x] and the limit point be x = 0
We note that LHL = –1 and RHL = 0, which are not equal, hence does not exist.
does not exist.
CAUTION
Never do like this  [– h] = [0] = 0
[– h] = [0] = 0
That is limit must be applied only after removing [] sign.
The limits evaluated earlier were not checked for LHL and RHL because it was assumed already that the limit of those functions exist. Actually, for the algebraic and transcendental functions we encounter, the limits exist. Mostly those functions, which are piecewise defined or composite functions need to be tested for LHL and RHL, specially at those points, where the definition of the function is changing.
CONTINUITY
Geometrically, a function f(x) is said to be continuous in an interval if its graph y = f(x) is a continuous curve in that interval.
CAUCHY'S DEFINITION
Let f be a real function and a be in the domain of f. We say f is continuous at a, if 
Hence f(x) is continuous if  exists and equals f (a).
exists and equals f (a).
The function f(x) is said to be continuous at x = a from left if 
The function f(x) is said to be continuous at x = a from right if
DISCONTINUITY OF A FUNCTION
A function f(x), which is not continuous at a point x = a, is said to be discontinuous at x = a.
The function f(x) can be discontinuous at a point x = a in any one of the following ways.
- f(a) is not defined
- Either
or both non existing or infinite
- LHL and RHL both exist but unequal, i.e.
- LHL and RHL both exist and equal but not equal to f(a), i.e.,
This particular kind is called REMOVABLE DISCONTINUITY
CONTINUITY OF A FUNCTION IN AN INTERVAL
- A function f(x) is said to be continuous in an open interval (a, b), if f(x) is continuous at every point of the interval.
- A function f(x) is said to be continuous in a closed interval [a, b] if f(x) is continuous in (a, b). In addition f(x) is continuous at x = a from right and f(x) is continuous at x =b from left.
FUNDAMENTAL THEOREMS ON CONTINUITY
- If f and g are continuous functions, then
- f ± g, fg are continuous
- cf is continuous, c is a constant
is continuous at those points where g(x) ≠ 0.
- If g is continuous at a point ‘a’ and f is continuous at g(a), then fog is continuous at a.
- If f is continuous in [a, b], then it is bounded in [a, b] i.e., there exist m and M such that
m and M are called minimum and maximum values of f(x) respectively in the interval [a b]
- If f is continuous in [a, b], then f assumes at least once every values between minimum and maximum values of f(x)
Thus or range of
f(x) = [m, M] if x∈[a b]
SOME CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS
- Every constant function is continuous at all points
- The identity function in continuous at all points
- Every polynomial function is continuous at all points
- f(x) = sin x and f(x) = cos x are continuous at all points
- f(x) = ax, a > 0, a ≠ 1 is continuous at all points
- Rational function is continuous at all points in its domain that is
is continuous at all points, where g(x) ≠ 0, f and g are polynomials.
- f(x) = log x is continuous if x > 0
- f(x) = tan x and f(x) = sec (x) are continuous at all points provided
- f(x) = cot x and f(x) = cosec x are continuous at all points provided
.
- f(x) = | x – a | is continuous at all points.
- f(x) = [x] is continuous at all points except x∈ I.
DIFFERENTIABILITY (OR DERIVABILITY) OF A FUNCTION
A function f (x) is said to be differentiable at a point 'a' in its domain, if the limit 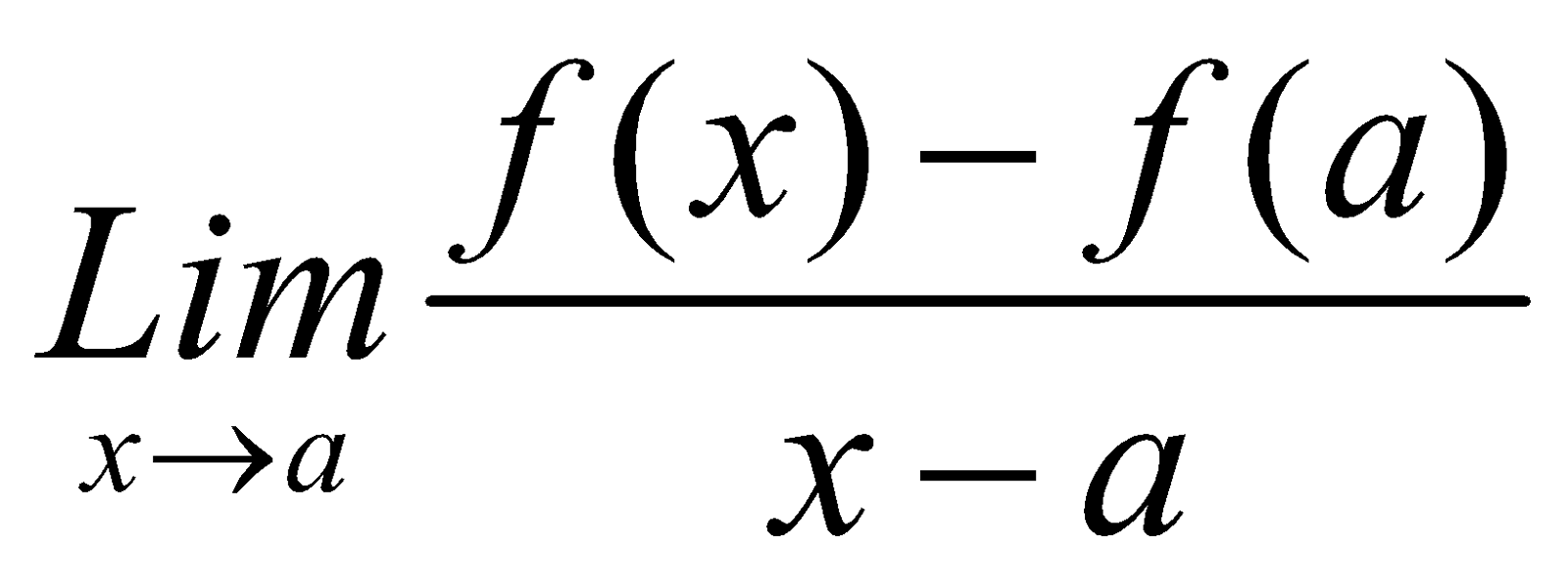 exists finitely. If this limit exists, it is called the derivative of f (x) at x = a, symbolically denoted by f’ (a) or D f (a).
exists finitely. If this limit exists, it is called the derivative of f (x) at x = a, symbolically denoted by f’ (a) or D f (a).
Hence, the function f (x) is differentiable at x = a
if and only if  exists finitely
exists finitely
that is, if and only if 
If the left hand limit 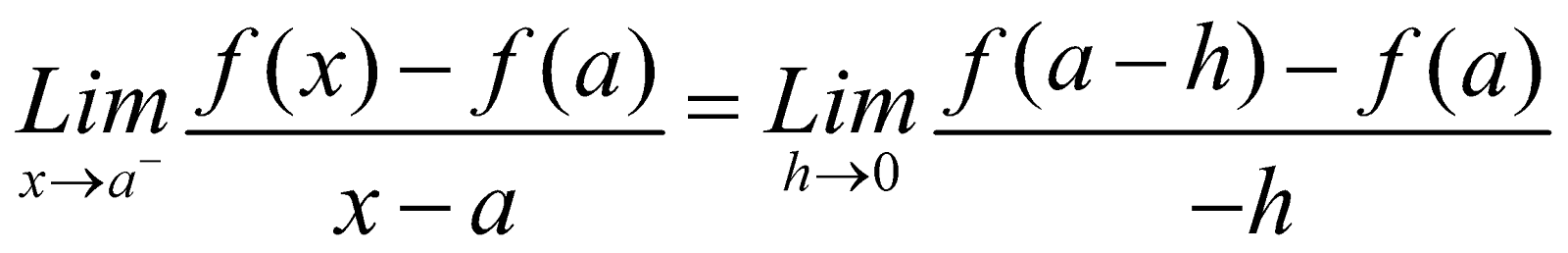 , h > 0 exists finitely, it is called Left Hand Derivative (LHD) at x = a and symbolically denoted by Lf’ (a) or f’ (a–) or f’(a – 0) or LDf(a).
, h > 0 exists finitely, it is called Left Hand Derivative (LHD) at x = a and symbolically denoted by Lf’ (a) or f’ (a–) or f’(a – 0) or LDf(a).
If the right hand limit  exists finitely, it is called Right Hand Derivative (RHD) at x = a and symbolically denoted by Rf’ (a) or f’(a+) or f’(a + 0) or RDf(a)
exists finitely, it is called Right Hand Derivative (RHD) at x = a and symbolically denoted by Rf’ (a) or f’(a+) or f’(a + 0) or RDf(a)
For example : Let us check the differentiability of f (x) = |x| at x = 0
[As h > 0, ∴ |h| = | –h| = h]
Thus, LHD ≠ RHD. Hence, f(x) = |x| is not differentiable at x = 0.
DIFFERENTIABILITY IN AN INTERVAL
A function f (x) is said to be differentiable in an interval (a, b) if f (x) is differentiable at every point of this interval (a, b).
A function f (x) is said to be differentiable in a closed interval [a, b], if f (x) is differentiable in (a, b), in addition f (x) is differentiable at x = a from right and differentiable at x = b from left.
RELATION BETWEEN CONTINUITY AND DIFFERENTIABILITY
- If a function f (x) is differentiable at x = a then f (x) is necessarily continuous at x = a.
- Converse of (1) is not necessarily true. That is, if a function f (x) is continuous at x = a, it is not necessarily differentiable at x = a. For example, f (x) = |x| is continuous at x = 0 but not differentiable at x = 0.
- If f (x) is not continuous at x = a, then f (x) is not differentiable at x = a.
GEOMETRICAL MEANING OF DIFFERENTIABILITY
Let y = f (x) be a function and 'a' be a point in the domain. Let P be the point (a, f (a)) on the curve. Let Q (x, f(x)) be an arbitrary point on the curve then the expression  represents the slope of the secant joining P and Q.
represents the slope of the secant joining P and Q.
Thus, the slope of secant joining
As we take the limit x → a, the point M approaches to N. That is the point Q approaches to P. At the limiting case, when Q is infinitesimally close to P, the chord PQ becomes a tangent
∴ f’(a) represents the slope of tangent at the point x = a
If a function is not differentiable at x = a, then either the tangent at x = a is vertical or the curve has no unique tangent at x = a, i.e., f (x) has a corner at x = a.







