ELLIPSE AND HYPERBOLA
ELLIPSE : THE STANDARD EQUATION
The equation of an ellipse in the standard form is given by , where a and b are constants related according to the relation.
, where a and b are constants related according to the relation.
e is the eccentricity of the ellipse.
- This ellipse has Focus S at (ae, 0).
- Directrix is
.
- The centre C of ellipse lies at origin.
According to definition of ellipse
SP = ePM, where e < 1.
EXISTENCE OF A SECOND FOCUS AND SECOND DIRECTRIX
Since, the ellipse is symmetrical about the y-axis also, therefore similar to points S and Z, such that CS = ae,
CZ = , we may have points S' and Z' symmetrically opposite to centre C such that CS' = CS = ae and CZ' = CZ =
, we may have points S' and Z' symmetrically opposite to centre C such that CS' = CS = ae and CZ' = CZ =  .
.
CZ =
S' will also be a focus with coordinates (–ae, 0) and a line through Z' perpendicular to axis will be corresponding directrix, with equation x =  .
.
Thus an ellipse has two foci (±ae, 0) and two directrics  .
.
OTHER DEFINITIONS
Let ........(i) be the equation of an ellipse.
........(i) be the equation of an ellipse.
where ......... (ii) [a > b]
......... (ii) [a > b]
- Major Axis : Intercept of the ellipse on the axis, (AA') is called the major axis. Thus Major Axis AA' = 2a.
- Minor Axis : Intercept of the ellipse on the y-axis (or a line perpendicular to the axis through the centre), BB' is called the minor axis. Thus Minor Axis BB' = 2b.
- Eccentricity :
- Focal Distances : Let P (x1, y1) be any point on the ellipse then SP = ePM =
= a – ex1 and
S'P = ePM' =  = a + ex1. The sum of the focal distances SP + S'P = 2a = major axis.
= a + ex1. The sum of the focal distances SP + S'P = 2a = major axis.
∴ The sum of focal distances of any point on the ellipse is a constant equal to major axis.
An alternative definition of ellipse is thus "the locus of a point such that the sum of its distances from two fixed points is a constant is an ellipse".
- Diameter : A chord through the centre of ellipse (note that it is not the definition of diameter) is a diameter of the ellipse. Hence the equation of any diameter of the ellipse
is of the form y = mx.
The major axis is the largest diameter of the ellipse.
The minor axis is the smallest diameter of the ellipse.
- Latus Rectum :
The double ordinate through a focus is called the latus rectum. For the equation  of an ellipse,
of an ellipse,
the length of latus rectum = 
the equation of latus recta is x = ±ae
the coordinates of the extremities of latus recta are  and
and  .
.
PARAMETRIC EQUATION OF AN ELLIPSE
Let the equation of an ellipse be  .
.
- A circle drawn with diameter equal to the major axis of the ellipse is called its AUXILIARY CIRCLE. Clearly the equation of the auxiliary circle is x2 + y2 = a2.
- Let P be any point on the ellipse. Let the ordinate through P meets the auxiliary circle at Q. The angle θ that the radius vector CQ subtends with major axis is called the ECCENTRIC ANGLE of the point P.
Clearly the coordinates of Q are (a cosθ, a sinθ).
If the coordinates of P be (x, y), then CN = x = a cos θ and
Hence x = a cos θ, y = b sin θ, , always satisfy the equation of ellipse. It is called the parametric equation of the ellipse.
The coordinates of any point P on ellipse may be given as  θ being parameter.
θ being parameter.
STANDARD FORM OF THE ELLIPSE WHEN A < B
Consider the equation of ellipse  when a < b
when a < b
Then a2 = b2 (1 – e2)
For this ellipse :
- Centre : (0, 0)
- Vertices : (0, ±b)
- Foci : (0, ±be)
- Directrices : y =
- Major axis : 2b
- Minor axis : 2a
- Equation of major axis : x = 0
- Equation of minor axis : y = 0
- Latus rectum =
- Symmetry : It is symmetric about both axes.
EQUATION OF AN ELLIPSE WHEN THE CENTRE DOES NOT LIE ON THE ORIGIN BUT AXES ARE PARALLEL TO COORDINATE AXES
If the centre of the ellipse lies at (h, k) and the axes are parallel to coordinate axes then the equation of the ellipse is

If a > b, then major axis = 2a and minor axis = 2b the eccentricity e = 
If a < b, then major axis = 2b and minor axis = 2a the eccentricity e = 
The other results may be obtained by using shifting of origin.
POSITION OF A POINT RELATIVE TO AN ELLIPSE
Consider a point P(x', y') and an ellipse
S(x, y) = 
- The point P lies inside the ellipse of
or S(x', y') < 0.
- The point P lies outside the ellipse if S (x', y') > 0.
INTERSECTION OF A LINE AND AN ELLIPSE
Let y = mx + c be a straight line and  be an ellipse.
be an ellipse.
Then the length of the chord cut on the line is given by
PQ = 
RESULTS
- The straight line intersects the ellipse in two distinct points if
- The straight line touches the ellipse if
- The straight line neither touch nor intersect the ellipse if
.
- The straight line y = mx + c touches the ellipse
if
.
- The straight line
is always a tangent to the ellipse
, for any value of m. the coordinates of point of contact are
, where c =
.
- For a given value of m, two parallel tangents can be drawn to an ellipse.
- The equation of tangent to the ellipse
can be written as
.
EQUATION OF A TANGENT TO AN ELLIPSE AT A POINT ON IT
- The equation of tangent to the ellipse
at a point (x', y') on it is
.
- The equation of tangent to the ellipse
at a point
is
.
EQUATION OF THE PAIR OF TANGENTS
The equation of the pair of tangents drawn from a point P(x1, y1) to the ellipse  is SS1 = T2
is SS1 = T2
Where 
 and
and 
CHORD OF CONTACT
The equation of chord of contact of tangents drawn from a point P (x1, y1) to the ellipse  is T = 0, where
is T = 0, where 
EQUATION OF CHORD JOINING TWO POINTS
Let P  and Q
and Q  be two points on the ellipse.
be two points on the ellipse.
Then equation of PQ is given by
Then equation of PQ is given by
On simplifying we get,.
Which is the required equation of the chord PQ.
CHORD WITH A GIVEN MIDPOINT
The equation of the chord of the ellipse  with P (x1, y1) as its middle point is given by T = S1
with P (x1, y1) as its middle point is given by T = S1
where 
EQUATION OF NORMAL IN DIFFERENT FORMS
- Point Form : The equation of the normal to the ellipse
at the point (x1 , y1) is
- Parametric Form : The equation of the normal to the ellipse
at the point (a cos θ, b sin θ) is
- Slope Form : The equation of normal to the ellipse
in terms of slope 'm' is
IMPORTANT POINTS
- The coordinates of the feet of normals are
- Condition for Normality : The line y = mx + c is a normal to the ellipse
- In each of the above equations we can write a2 – b2 as a2e2 also.
- Number of Normals : In general, four normals can be drawn to an ellipse from a point in its plane, i.e, there are four points on the ellipse, the normals at which pass through a given point. These four points are called the co-normal points
- If α, β, γ, δ are the eccentric angles of the four points on the ellipse such that the normals at these points are concurrent, then (α + β + γ + δ) is an odd multiple of π.
- If α, β, γ are the eccentric angles of three points on the ellipse
, the normals at which are concurrent, then
HYPERBOLA : THE STANDARD EQUATION
The equation of a hyperbola in the standard form is given by
 ....(i)
....(i)
where a and b are constants related according to the relation  ",
",
e is the eccentricity of the hyperbola.
For the hyperbola (i), there are two foci S (ae, 0) and S' (–ae, 0) and correspondingly two directricies  and
and  respectively.
respectively.
The centre C of the hyperbola lies at the origin. According to the definition of the ellipse 
OTHER DEFINITIONS
Let  ...(i)
...(i)
be the equation of a hyperbola, where  ...(ii)
...(ii)
- Transverse Axis : Intercept of the hyperbola on the axis (AA') is called its transverse axis, the transverse axis, AA' = 2a.
- Conjugate Axis : Length BB' = 2b, on y-axis is called conjugate axis of the hyperbola. [Note that the hyperbola does not intersect the y-axis].
- Eccentricity :
- Focal Difference : Let P (x1, y1) be any point on the hyperbola then
The difference of the focal distances  = transverse axis
= transverse axis
∴ The difference of the focal distances of any point on the hyperbola is a constant, equal to transverse axis.
An alternative definition of hyperbola is thus "the locus of a point such that the difference of its distances from two fixed points is a constant is a hyperbola".
- Latus rectum : For the hyperbola
,
the length of latusrectum =
the equations of latus recta are 
the coordinates of the extremities of latus recta are  and
and  .
.
PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS OF HYPERBOLA
Hence x = a sec θ, y = b tan θ,  represents parametric equation of a hyperbola.
represents parametric equation of a hyperbola.
The coordinates of any point P on hyperbola may be given as (a secθ, b tanθ), θ being parameter.
EQUATION OF A CHORD JOINING TWO POINTS
Let P (a secθ, b tanθ) and Q (a secφ, b tanφ) be two points on the hyperbola. Then the equation of PQ is given by 
CONJUGATE HYPERBOLA
The hyperbola given by  and the hyperbola given by
and the hyperbola given by  or
or  are called conjugate of one another.
are called conjugate of one another.
- We have transverse axis of first = Conjugate axis of second and vice versa.
- If the eccentricity of two hyperbolas be e and e' respectively then
.
RECTANGULAR (OR EQUILATERAL) HYPERBOLA
If transverse axis = Conjugate axis, then the hyperbola is called a rectangular hyperbola.
The standard equation for a rectangular hyperbola becomes  [since a = b]
[since a = b]
The eccentricity of a rectangular hyperbola is always constant equal to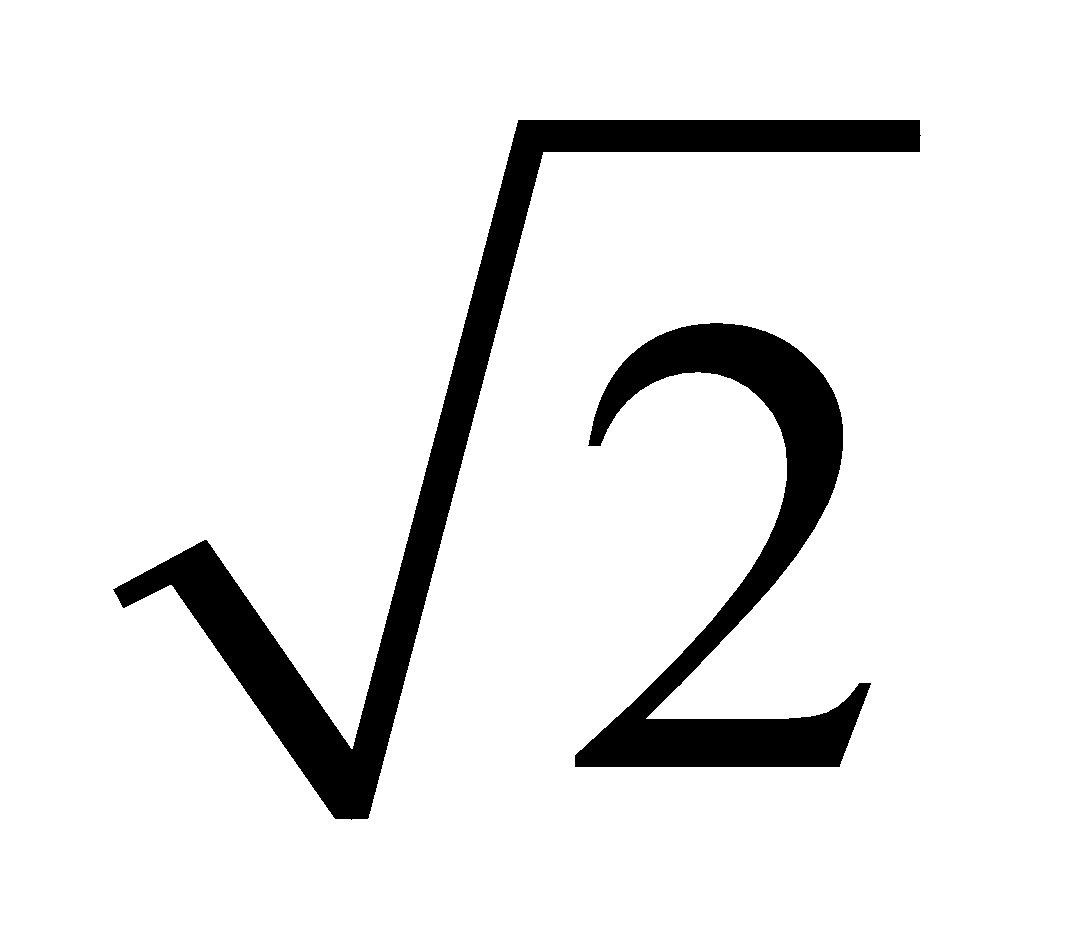 .
.
EQUATION OF A HYPERBOLA WHEN THE CENTRE DOES NOT LIE AT THE ORIGIN BUT THE AXES ARE PARALLEL TO COORDINATE AXES
If the centre of the hyperbola lies at a point (h, k) and the axes are parallel to the coordinate axes then the equation of the hyperbola is
- Transverse axis = 2a
- Conjugate axis = 2b
- Eccentricity
- Foci (h ± ae, k).
- Latus recta are x =
POSITION OF A POINT RELATIVE TO HYPERBOLA
Consider a point P(x', y') and the hyperbola be S(x, y) = .
.
- P lies within the hyperbola if S (x', y') > 0
- P lies without the hyperbola if S (x', y') < 0
PROPOSITIONS
All the results derived for the ellipse turn out to be the results for a hyperbola simply after replacing b2 by –b2. Hence
turn out to be the results for a hyperbola simply after replacing b2 by –b2. Hence
- The length of chord cut on the straight line y = mx + c is
.
- The straight line y = mx + c intersects the hyperbola in two distinct points if a2m2 – b2 – c2 > 0.
- The straight line y = mx + c touches the hyperbola if
.
- The straight line y = mx +c neither touch nor intersects the hyperbola if a2m2 – b2 – c2 < 0.
- The straight line y = mx ±
is always a tangent to the hyperbola provided
. The coordinates of the point of contact are
, where
.
- For a given value of m
, two parallel tangents can be drawn to a hyperbola.
- The equation of tangent to the hyperbola at a point (x', y') on it is
.
- The equation of tangent to the hyperbola at a point (a secθ, b tanθ) is
or
NUMBER OF TANGENTS FROM A POINT
Two tangents can be drawn from a point to a hyperbola. The two tangents are real and distinct or coincident or imaginary according as the given point lies outside, on or inside the hyperbola.
EQUATION OF THE PAIR OF TANGENTS
The equation of the pair of tangents drawn from a point p (x1, y1) to the hyperbola  is SS1 = T2
is SS1 = T2
where ,
, 
and 
DIRECTOR CIRCLE
It is the locus of points from which ⊥ tangents are drawn to the hyperbola. The equation of director circle of the hyperbola.
CHORD OF CONTACT
The equation of chord of contact of tangents drawn from a point P(x1, y1) to the hyperbola  is T = 0. where
is T = 0. where  .
.
CHORD WITH A GIVEN MIDPOINT
The equation of the chord of the hyperbola  with P (x1, y1) as its middle point is given by T = S1 where
with P (x1, y1) as its middle point is given by T = S1 where 
EQUATION OF NORMAL IN DIFFERENT FORMS
- Point Form : The equation of the normal to the hyperbola
at the point
is
- Parametric Form : The equation of the normal to the hyperbola
at the point
is
- Slope Form : The equation of normal to the hyperbola
in terms of slope 'm' is
Notes :
- The coordinates of the feet of normals are
- Number of Normals : In general, four normals can be drawn to a hyperbola from a point in its plane, i.e. there are four points on the hyperbola, the normals at which will pass through a given point. These four points are called the co-normal points.
- Tangent drawn at any point bisects the angle between the lines joining the point to the foci, whereas normal bisects the supplementary angle between the lines.
ASYMPTOTES OF HYPERBOLA
The lines  i.e
i.e  are called the asymptotes of the hyperbola.
are called the asymptotes of the hyperbola.
The curve comes close to these lines as  or
or  but never meets them. In other words, asymptote to a curve touches the curve at infinity.
but never meets them. In other words, asymptote to a curve touches the curve at infinity.
IMPORTANT RESULTS
- The asymptotes pass through the centre of the hyperbola.
- The angle between the asymptotes of
is
- A hyperbola and its conjugate hyperbola have the same asymptotes.
- The bisector of the angle between the asymptotes are the coordinate axes.
- Asymptotes are the diagonals of the rectangle passing through A, B, A', B' with sides parallel to axes.
- Any line drawn parallel to the asymptote of the hyperbola would meet the curve only at one point.
- The product of the perpendiculars from any point on the hyperbola
to its asymptotes is a constant equal to
.
RECTANGULAR HYPERBOLA
If asymptotes of the standard hyperbola are perpendicular to each other, then it is known as Rectangular Hyperbola.
Thus, or
or  is general form of the equation of the rectangular hyperbola
is general form of the equation of the rectangular hyperbola
Thus,
If we take the coordinate axes along the asymptotes of a rectangular hyperbola, then equation of rectangular hyperbola becomes xy = c2 , where c is any constant.
In parametric form, the equation of rectangular hyperbola is x = ct, y = c/t, where t is the parameter.
The point (ct, c/t) on the hyperbola xy = c2 is generally referred as the point 't'.
PROPERTIES OF RECTANGULAR HYPERBOLA, x2 – y2 = a2
- The equations of asymptotes of the rectangular hyperbola are
- The transverse and conjugate axes of a rectangular hyperbola are equal in length.
- Eccentricity,
PROPERTIES OF RECTANGULAR HYPERBOLA xy = c2
- Equation of the chord joining 't1' and 't2' is : x + yt1t2 – c (t1 + t2) = 0
- Equation of tangent at (x1, y1) is :
or
- Equation of tangent at 't' is
or x + yt2 = 2ct
- The slope of the tangent at the point (ct, c/t) is -1/t2, which is always negative. Hence tangents drawn at any point to xy = c2 would always make an obtuse angle with the x-axis.
- Point of intersection of tangents at 't1' and 't2' is :
- Equation of normal at (x1, y1) is :
- Equation of normal at 't' is :
- The slope of the normal at the point (ct, c/t) is t2, which is always positive. Hence normal drawn to xy = c2 at any point would always make an acute angle with the x-axis.
- The equation of the chord of the hyperbola xy=c2 whose middle point is (x1, y1) is T = S1 i.e. xy1+ x1y = 2x1y1







