PURIFICATION, QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
The organic compounds obtained from natural sources or synthesised in the lab are often contaminated with impurities. They are purified by specialised methods
METHODS OF PURIFICATION OF SOLIDS
- Crystallisation: A saturated solution of impure substance is prepared in hot solvent and is heated with vegetable or animal charcoal which adsorbs the impurities. The solution is filtered while hot through a hot water funnel. The filtrate on cooling deposits crystals of pure compound. Success of the process depends upon the selection of the solvent. The impurities must be least soluble while hot and most-soluble while cold. The quick cooling gives tiny but pure crystals while slow cooling gives bigger but impure crystals. When crystal formation is initiated by adding crystals of substance it is called “Seeding”.
- Fractional crystallisation : It is based on the differential solubilities of different compounds in a solvent. The compound having less solubility crystallises out first on cooling leaving behind others in solution. Sometimes mixture of two solvents eg. Alcohol & water; Chloroform & Petroleum ether, Alcohol or ether give better results.
- Sublimation: Some solids directly pass into vapour when heated and vapour directly pass into solid when cooled without the intermediate formation of liquid. This is known as sublimation. The substances which sublime can be purified by this method provided the impurities present do not sublime. Camphor, naphthalene, anthracene, benzoic acid, phthalic anhydride and anthraquinone are purified by sublimation.
METHODS OF PURIFICATION OF LIQUIDS
- Simple distillation: The vaporisation of a liquid by heating and subsequent condensation of vapours by cooling is known as distillation. The liquids boiling under ordinary conditions of temperature and pressure without decomposition and containing non volatile impurities are purified by simple distillation.
- Fractional distillation: It is employed for separating two or more volatile liquids having boiling points close to each other eg. acetone (bpt 60ºC) and methanol (bpt 65ºC). The vapours of the liquids pass through the fractionating column which provides greater space for their cooling. The vapours of high boiling fractions condense and fall back into distillation flask. The process is repeated till fractions of high volatility go up followed by of lower volatility. They are collected separately.
- Distillation under reduced pressure or vacuum distillation: Some liquids decompose when heated to their boiling points eg. glycerol. Such liquids can be purified by distillation under reduced pressure much below their boiling points. The lower the pressure lower is the boiling point and vice versa.
- Steam distillation: The liquids insoluble in water, steam volatile in nature, having high molecular weight and having high vapour pressure are purified by steam distillation provided the impurities present are not steam volatile.
Theory of steam distillation: The liquid boils when its vapour pressure becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure. For a mixture of liquid (pl) and steam (ps) we have at boiling point P = pl + ps pl = (P – ps)
Hence liquid will boil at lower temperature than its normal boiling point. Examples Aniline, o-nitrophenol, bromobenzene, salicylaldehyde, essential oils etc.
CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHODS
It was discovered by Tswett (1906) and developed by Kuhn, Winterstein and Karrer.
PRINCIPLE
Selective adsorption or distribution of various components of mixture between the two phases - fixed phase and mobile phase.
CLASSIFICATION
- Adsorption chromatography: Fixed phase - Solid or ion exchange resin
Mobile phase - Liquid or gas
Hence it is further known as liquid - solid chromatography, gas-solid chromatography or ion exchange chromatography.
- Partition Chromatography: Fixed phase - liquid supported on inert solid
Mobile phase - liquid or gas
Hence we have liquid - liquid partition chromatography and liquid gas partition chromatography
Paper chromatography is the example of partition chromatography
COLUMN CHROMATOGRAPHY
Example of Adsorption chromatography
Adsorbents used are: alumina, silica gel, cellulose powder, sucrose, animal charcoal, magnesium oxide or kieselguhr etc.
Liquid Solvents used are : benzene, petroleum ether, chloroform, alcohol etc.
When the solvent is poured over the mixture present at the top of a column packed with adsorbent the components are separated into number of layers called Zones, bands or chromatograms due to preferential adsorption. The process being known as development.
Elution : The continuous pouring of solvent from the top of column is known as elution or running of column.
Solvent : It is known as eluent.
The most weakly adsorbed component is eluted first by least polar solvent while more strongly adsorbed component is eluted later by highly polar solvents.
CHEMICAL METHODS
The substance to be purified is treated with a suitable chemical reagent to form a stable derivative (impurities being unreacted). It is then separated by suitable method and decomposed to get the pure compound. Examples:
- Mixture of amines (1º, 2º and 3º) is separated by Hinsberg’s method and Hoffmann’s method.
- Acetic acid from pyroligneous acid is separated by forming Ca salt.
- Acids are separated by forming Na derivatives with NaHCO3.
- Commercial benzene contains thiophene which is removed by forming sulphonic acid derivative.
- Carbonyl compounds are purified by forming bisulphite derivative.
- Absolute alcohol is obtained from rectified spirit by quicklime process and azeotropic distillation.
EXTRACTION
The process of removing a substance from its aqueous solution by shaking with a suitable solvent is known as extraction. (partition law) The greater the number of operations the greater is the recovery of substance. Soxhlet extractor is used for continuous extraction.
DRYING OF ORGANIC SUBSTANCES
Stable solids may be dried in a steam or air oven; by heating on a free flame. In a vacuum desicator using anhy. CaCl2, conc H2SO4 or P2O5 etc.
Alcohols are dried over : Quick lime, anhy. K2CO3, MgSO4 or Na2SO4
Aldehydes and Ketones : Anhy. MgSO4, Na2SO4 or CaCl2
Organic acids: Anhy. MgSO4, Na2SO4 or P2O5
Organic bases: Solid KOH, Quick lime or Soda lime
CRITERIA OF PURITY
- Mixed melting point: The purified substance is mixed with pure substance (100%) and melting point is taken. If it is sharp the substance is pure otherwise not. Impurities lower the melting point.
- Boiling Point: The boiling point of a liquid is defined as the temperature at which its vapour pressure becomes equal to atmospheric pressure. Sharp and concordant boiling point is the criteria of purity of organic substance. Impurities increase the boiling point.
DETECTION OF CARBON AND HYDROGEN
DETECTION OF NITROGEN
- Soda-lime test
organic compound + NaOH smell of NH3 ↑
(Not reliable since –NH2, –NO2 and – N = N-groups do not respond).
- Lassaigne’s test
Common for N, S and X (halogens)
Lassaigne’s filtrate or sodium extract is prepared by fusing the organic compound with Na in ignition tube. Fused mass is dissolved in water, boiled and filtered. The filtrate is sodium extract which contains
Na + C + N NaCN (Sodium cyanide)
NaCN (Sodium cyanide)
2Na + S Na2S (Sodium sulphide)
Na2S (Sodium sulphide)
Na + X NaX (Sodium halide)
NaX (Sodium halide)
Na + C + N + S NaCNS (Sodium Sulphocyanide)
NaCNS (Sodium Sulphocyanide)
Test for nitrogen
Sod. extract + freshly prepared FeSO4 solution + FeCl3 solution + dil. H2SO4 green or blue colouration or sometimes blood red colour
2 NaCN + FeSO4 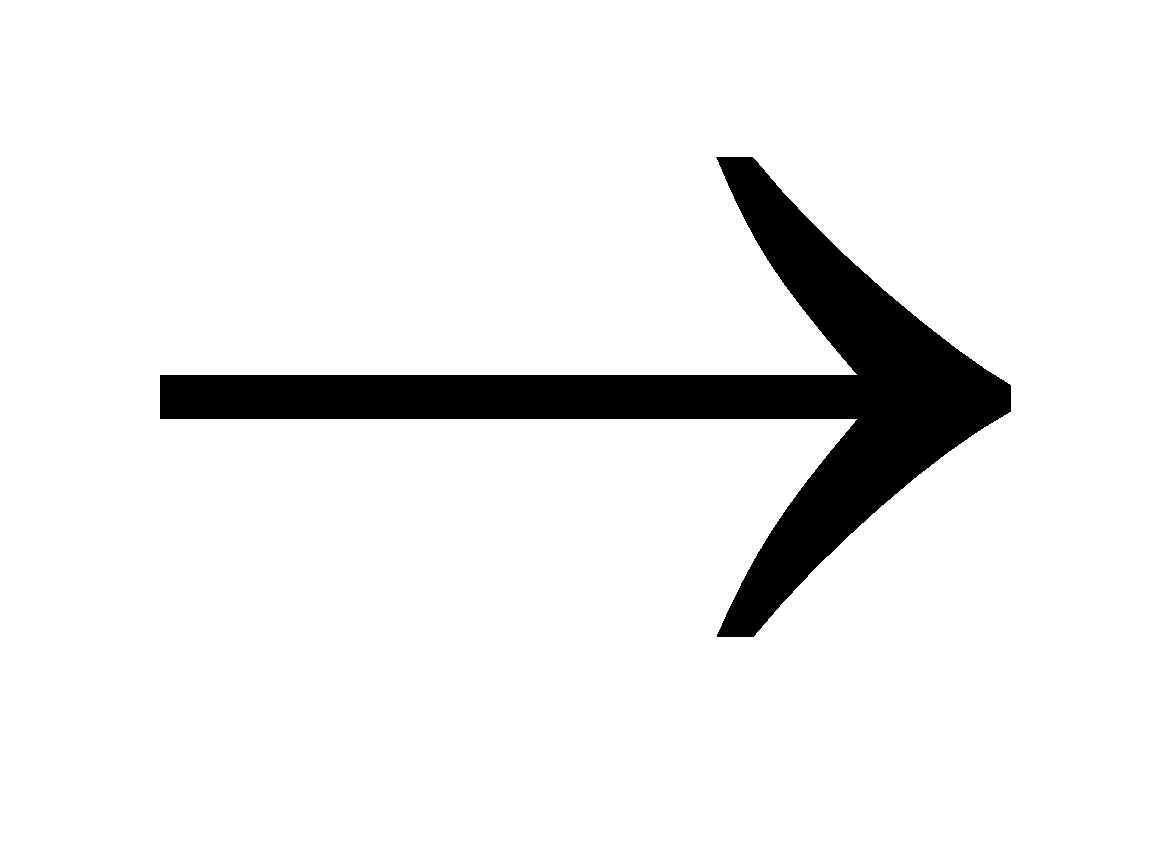 Fe(CN)2 + Na2SO4
Fe(CN)2 + Na2SO4
4 NaCN + Fe(CN)2 Na4 [Fe(CN)6]
Na4 [Fe(CN)6]
3 Na4[Fe(CN)6] + 4 FeCl3 Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3+12NaCl
Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3+12NaCl
Ferric ferrocyanide (prussian blue)
FeCl3 + 3 NaCNS 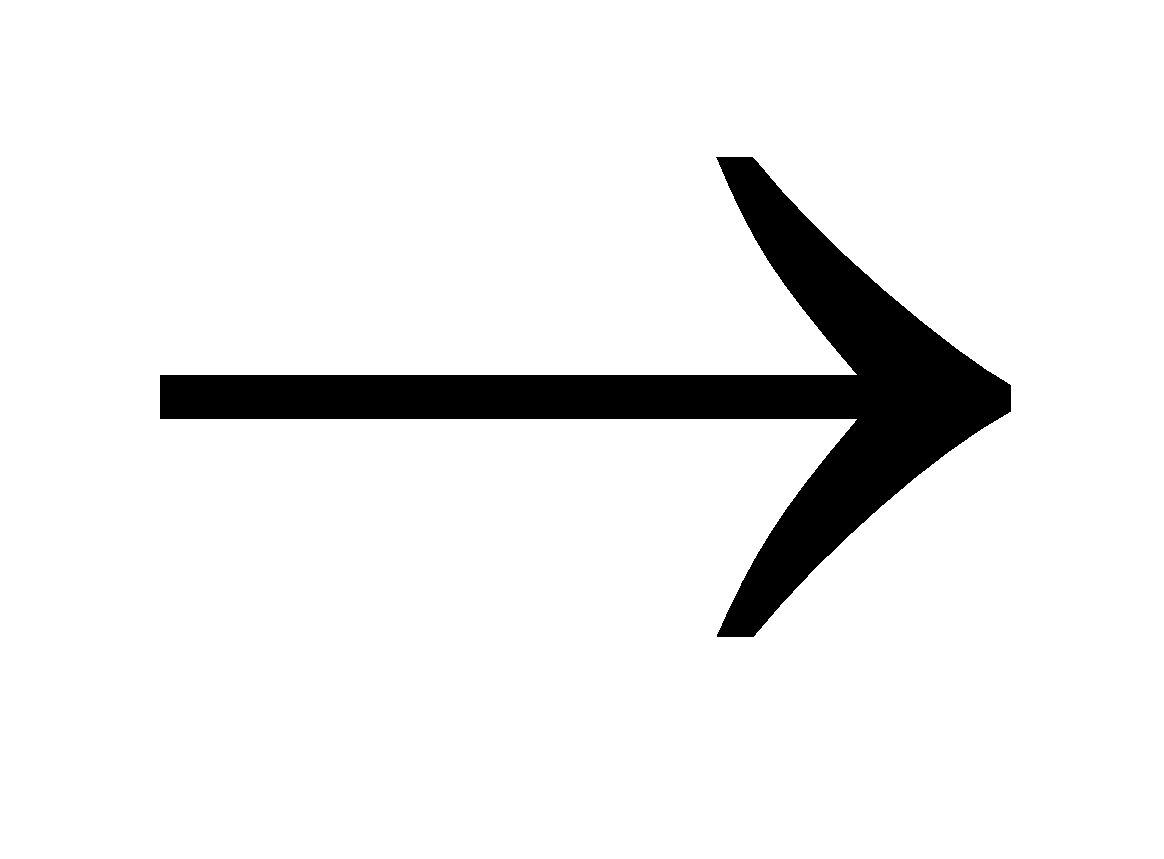 Fe(CNS)3 + 3NaCl
Fe(CNS)3 + 3NaCl
Ferric sulphocyanide (Blood red)
(NH2.NH2 and diazo compounds do not give this test, diazo compounds are decomposed to give N2 and NH2.NH2 does not contain C)
Test for sulphur
Test for halogens
Sod. extract + Conc. HNO3 + AgNO3 Solution
- If white precipitate soluble in NH4OH
Cl– present
- If light yellow precipitate sparingly soluble in NH4OH
Br– present
- If yellow precipitate insoluble in NH4OH I– present
- Function of Conc. HNO3 : It decomposes NaCN and Na2S to avoid their interference
- Layer test for bromine and iodine:
Sod Extract 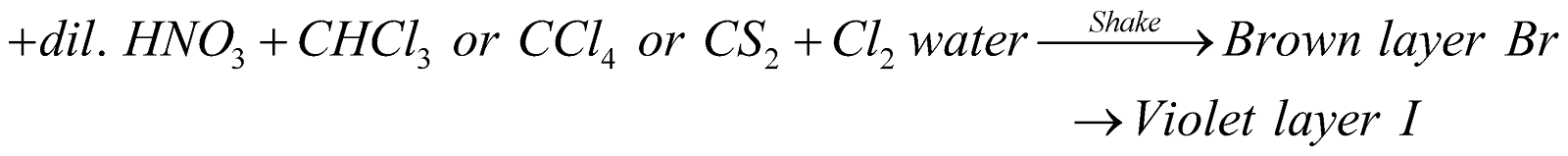
- Beilstein's test: Organic compounds containing halogens when heated over Cu wire loop, give blue or green colour flame due to formation of volatile copper halides. (Not reliable since thiourea, urea, pyridine and organic acids also give this test)
DETECTION OF PHOSPHORUS
Organic compound + fusion mixture (Na2CO3 + KNO3) or Na2O2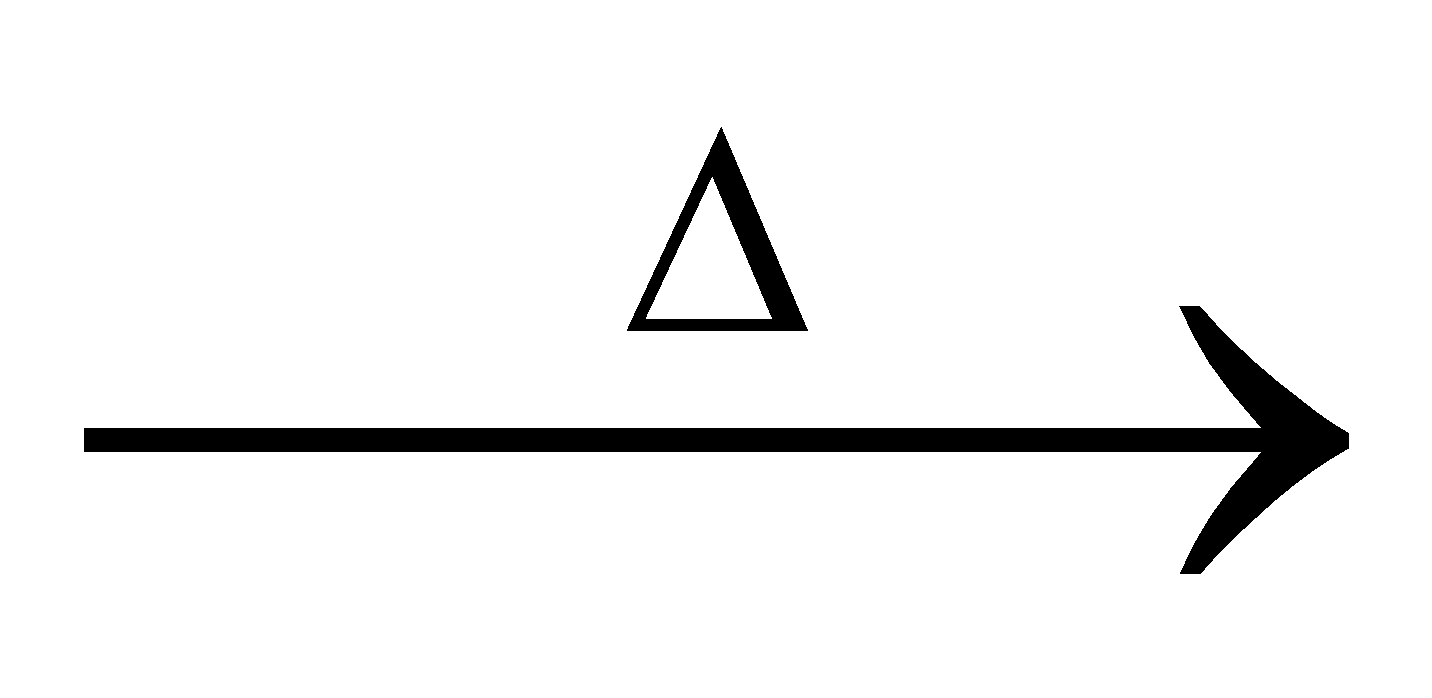 fused mass
fused mass 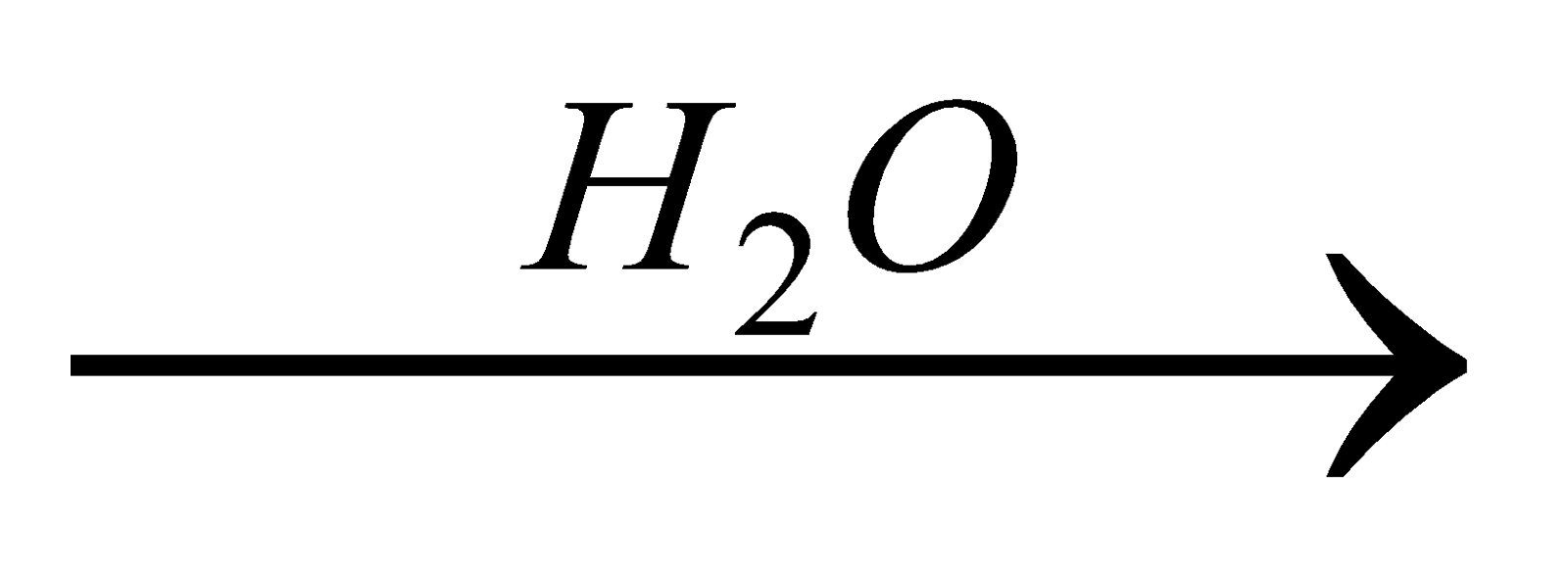 water extract + conc. HNO3 + ammonium molybdate yellow ppt.
water extract + conc. HNO3 + ammonium molybdate yellow ppt.
Amm. molybdate
Amm. phosphomolybdate (yellow ppt.)
ESTIMATION OF ELEMENTS
ESTIMATION OF CARBON AND HYDROGEN (LIEBIG’S METHOD)
By knowing the amount of CO2 and H2O from known weight of organic compound, the percentage of carbon and hydrogen can be calculated.
- The water is absorbed in anhydrous CaCl2 or anhydrous magnesium perchlorate
- The carbon dioxide is absorbed in Saphnolite (a resion) or Ascarite (NaOH on asbestos) or KOH
- When organic compound contains nitrogen, oxides of nitrogen (NO and N2O etc) are formed and absorbed by caustic potash. These are removed by the use of bright copper gauge
Nitrogen is not absorbed by KOH solution.
- When organic compound contains halogens they are removed by using silver gauge by forming non volatile silver halide
- When sulphur is present, it is removed by forming lead sulphate by using fused lead chromate and halogens form lead halides.
- Percentage of carbon =
- Percentage of hydrogen =
ESTIMATION OF NITROGEN
DUMA’S METHOD
This method can be applied to all nitrogenous compounds. Though tedious better than Kjeldahl's method.
The mixture of gases is passed in KOH all gases except N2 are absorbed. Nitrogen is collected over KOH and its volume at NTP is measured.
KJELDAHL’S METHOD
Organic compound 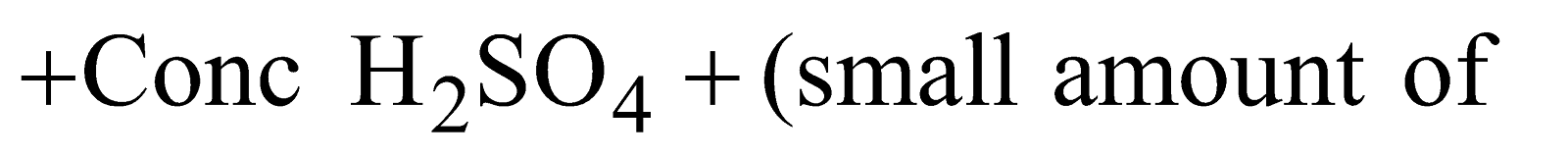


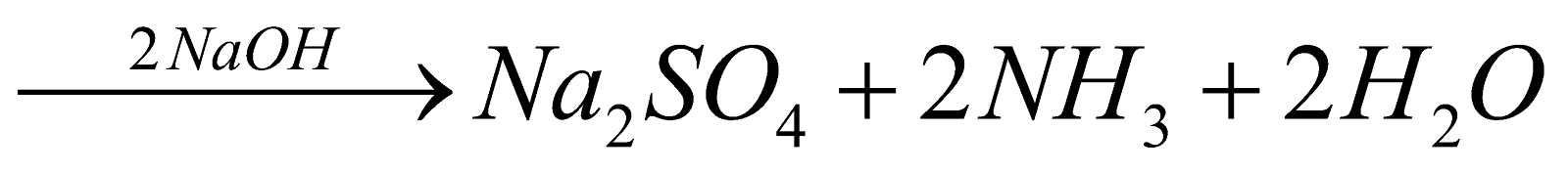
Ammonia is passed into H2SO4 or HCl of known volume and normality. The volume of acid neutralised by NH3 is calculated by neutralising the acid left by NaOH solution.
Percentage of Nitrogen 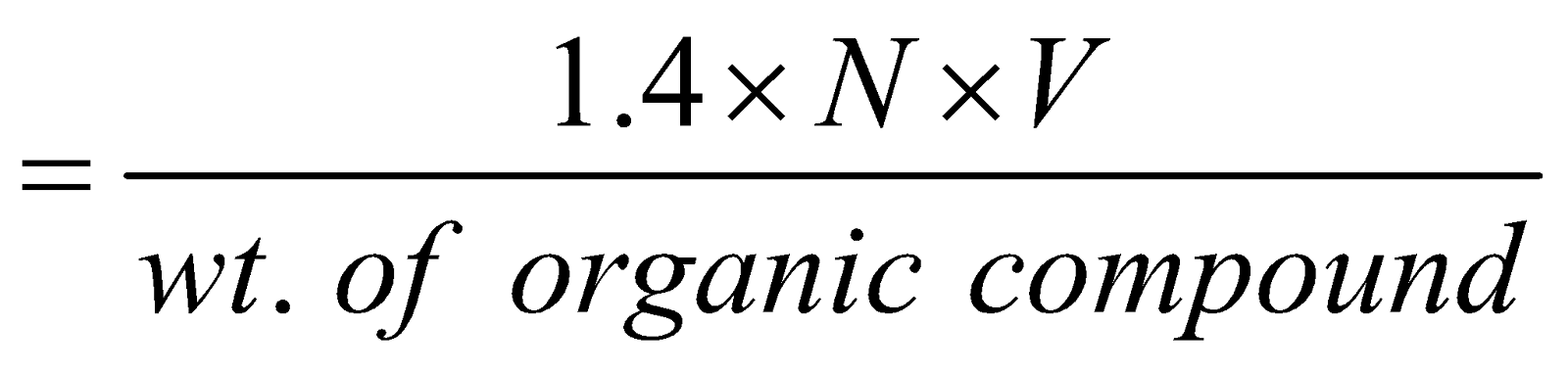
N = normality of acid, V = volume of acid in ml. neutralised by ammonia
In practice K2SO4 is added to raise the bpt of H2SO4 and CuSO4 or Hg is added to catalyse the reaction)
Kjeldahl's method is not reliable. The results obtained are generally low. It cannot be applied to compounds in which nitrogen is directly linked to oxygen such as nitro, nitroso, azo and nitrogen present as in pyridine. It is used for estimating nitrogen in food , fertilizers and agricultural products.
ESTIMATION OF HALOGENS
CARIUS METHOD
Organic compound + Fuming HNO3 + AgNO3 AgX.
AgX.
Organic compound + Fuming HNO3 + AgNO3
It is estimated gravimetrically
SCHIFF'S AND PIRIA METHOD
Organic compound (small amount) +
AgX is estimated as in Carius method
This method is not suitable for volatile halides for iodides only Na2CO3 is used as lime forms calcium iodate which is insoluble in water.
STEPANOV METHOD
Excess of alcohol distilled off and solution treated with 6N HNO3 and filtered. AgX is precipitated by adding AgNO3 which is filtered, washed and weighted.
ESTIMATION OF SULPHUR
Organic compound + oxidising agent (fuming HNO3 in Carius method)  H2SO4
H2SO4 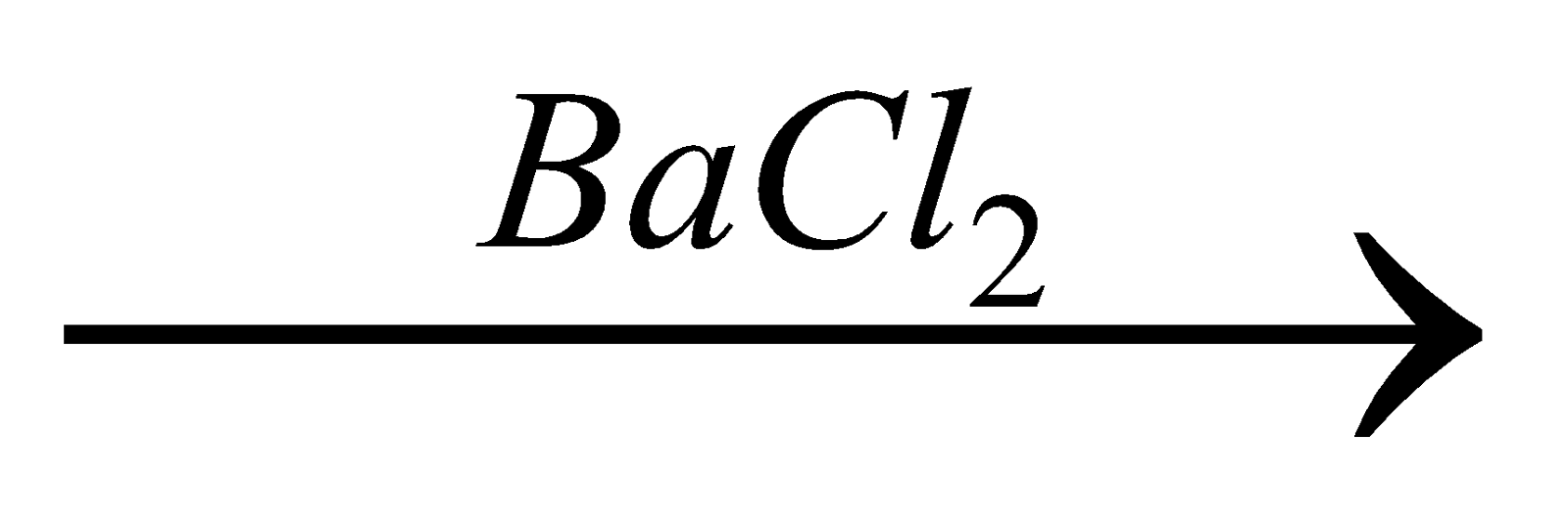 BaSO4.
BaSO4.
It is estimated gravimetrically
HNO3 in Carius method
Alk.KMnO4 in Messenger's method
Alk.KMnO4 in Messenger's method
Na2O2 + Na2CO3 in Asboth's method
ESTIMATION OF PHOSPHORUS
By Carius method
Organic Compound + Fuming nitric acid  H3PO4
H3PO4  MgNH4PO4
MgNH4PO4
DETERMINATION OF MOLECULAR WEIGHT
PHYSICAL METHODS
- Vapour Density method:
- Victor's Meyer
- Dumas
- Hofmann's
- Freezing point
- Boiling method.
VAPOUR DENSITY METHOD
- Victor Meyer’s method : for volatile substances: A known weight of the volatile substance is vaporised by heating in Victor Meyer’s tube and the equivalent volume of the air displaced is calculated at NTP after proper correction of aqueous tension. Vapour density is given by following relation.
At N.T.P. 22.4 Litre of Hydrogen = 2 g.
M. Wt = 2 × VD
- Duma's method : Weight of known volume of the vapour of the substance in a glass bulb at an elevated temperature is noted.
- Hofmann's method : A known weight of the substance is vaporised above a mercury column in a barometric tube and volume of the vapours formed is noted.
In Dumas and Hofmann method the calculations are same as Victor Meyer’s method.
FREEZING POINT METHOD OR CRYOSCOPIC METHOD
M = molecular weight of the substance
Kf = molal depression constant
w = Weight of the substance
W = weight of the Solvent
BOILING POINT METHOD OR EBULLIOSCOPIC METHOD
M = molecular weight of the substance
Kb = molal elevation constant
w = weight of the substance
W = weight of solvent
CHEMICAL METHODS
- Silver Salt method for Acids
- Platinic Chloride method for Bases
- Volumetric method for Acids and Bases
SILVER SALT METHOD FOR ACIDS
Mol. wt. of an acid is given by the following expression
Mol. wt. of acid = Equivalent wt × basicity
Mol. wt. of acid 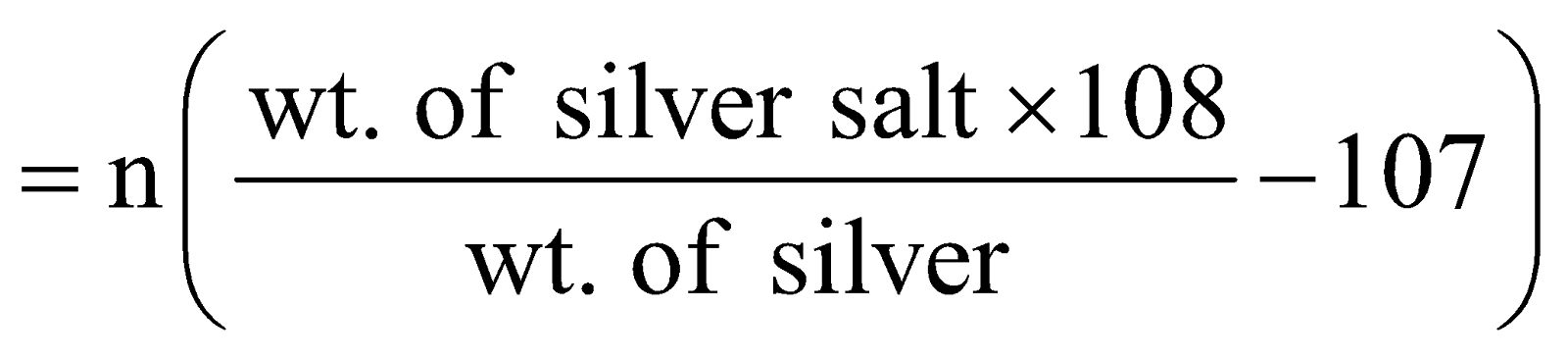
n = basicity of the acid
PLATINIC CHLORIDE METHOD FOR BASES
Mol wt. of a base is given by the following expression
Mol. wt. of base = Eq. wt. of base × Acidity
Mol. wt. of base 
n = Acidity of the base
MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF AN ACID AND A BASE BY VOLUMETRIC METHOD
Equivalent weight of an acid is that weight of acid which is neutralised by 1 geq. of a base Equivalent weight of a base is that weight of base which is neutralised by 1 geq of an acid
where N = Normality of acid of base
V = Volume of acid or base in ml.
EMPIRICAL AND MOLECULAR FORMULA
Empirical formula: It represents the relative number of atoms of each element present in one molecule of the compound.
Molecular formula: It represents the actual number of atoms of each element present in one molecule of the compound.
CALCULATION OF EMPIRICAL FORMULA
- Divide the percentage of each element by the atomic weight of the element.
- Divide all the numbers by lowest number obtained in the first step.
- Convert them in whole numbers if obtained in fractions by multiplying them by common factor.
CALCULATION OF MOLECULAR FORMULA
EUDIOMETRY
Determination of molecular formula of gaseous hydrocarbon by exploding with excess of oxygen in a eudiometer is known as Eudiometry.
Hydrocarbon (known volume) + O2 (Exces known volume)
It is absorbed by alkaline pyrogallol. Hence volume of O2 reacted can be known and molecular formula can be calculated with the help of following equation
IDENTIFICATION OF SOME ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
- Aldehydes : Give silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent and red precipitate with Fehling soln. and pink colour with Schiff's reagent.
Remember benzaldehyde do not respond to Fehling solution. - Ketones : Give orange ppt with 2, 4 dinitrophenyl hydrazine solution.
- Acids : Give effervescence with
- Alcohols : Give wine red colour with ceric ammonium nitrate.
- Phenols : Give deep colour change with 1% sol.
- Ethers : with conc. HI give alcohol and alkyl iodide. With excess HI, RI is the product.
- Methyl ketones : Give iodoform with and NaOH.
- Esters : When added to very dil soln. of NaOH containing phenolphthalein, the pink colour is discharged.
- Aliphatic 1° amines : Give alcohols with and HCl.
- Aromatic 1° amines : Give diazo compound with and HCl.
(Note: must be linked to benzene nucleus)
- 2° amines : Give highly nitrosamine with and HCl.
- 3° amines : Salt only salt with and HCl
- Cyanides : On reduction with Na + give 1° amines. On hydrolysis give acids
- Isocyanide : On reduction with Na + give 2° amines. On acid hydrolysis give 1° amine and formic acid.
- 1° amine : Give isocyanides with + NaOH, which have unpleasant odour.
- Nitro compounds : Give 1° amine with Sn + HCl.
- Amides : Give when heated with NaOH.
- Anilides : They are hydrolysed to 1° amines.










