CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
The compounds containing the carboxyl functional group  are called Carboxylic acids. The word carboxyl is a combination of two words carbonyl (>C=O) and hydroxyl (–OH).
are called Carboxylic acids. The word carboxyl is a combination of two words carbonyl (>C=O) and hydroxyl (–OH).
CLASSIFICATION
Depending upon the number of –COOH groups they are classified as
- Monocarboxylic acids: containing one -COOH group
- dicarboxylic acids: containing two -COOH groups and so on
- Fatty acids: Aliphatic monocarboxylic acids are commonly called fatty acids because higher members are obtained by the hydrolysis of oils and fats.
NOMENCLATURE
There are three ways of naming carboxylic acids
Common System
The common names are derived from the source of acids.
Formula Common name Source
HCOOH Formic acid Red ant (formica)
CH3COOH Acetic acid Vinegar (acetium)
C3H7COOH Butyric acid Butter (butyrum)
The position of substituents are indicated by Greek letters  ,
,  ,
, 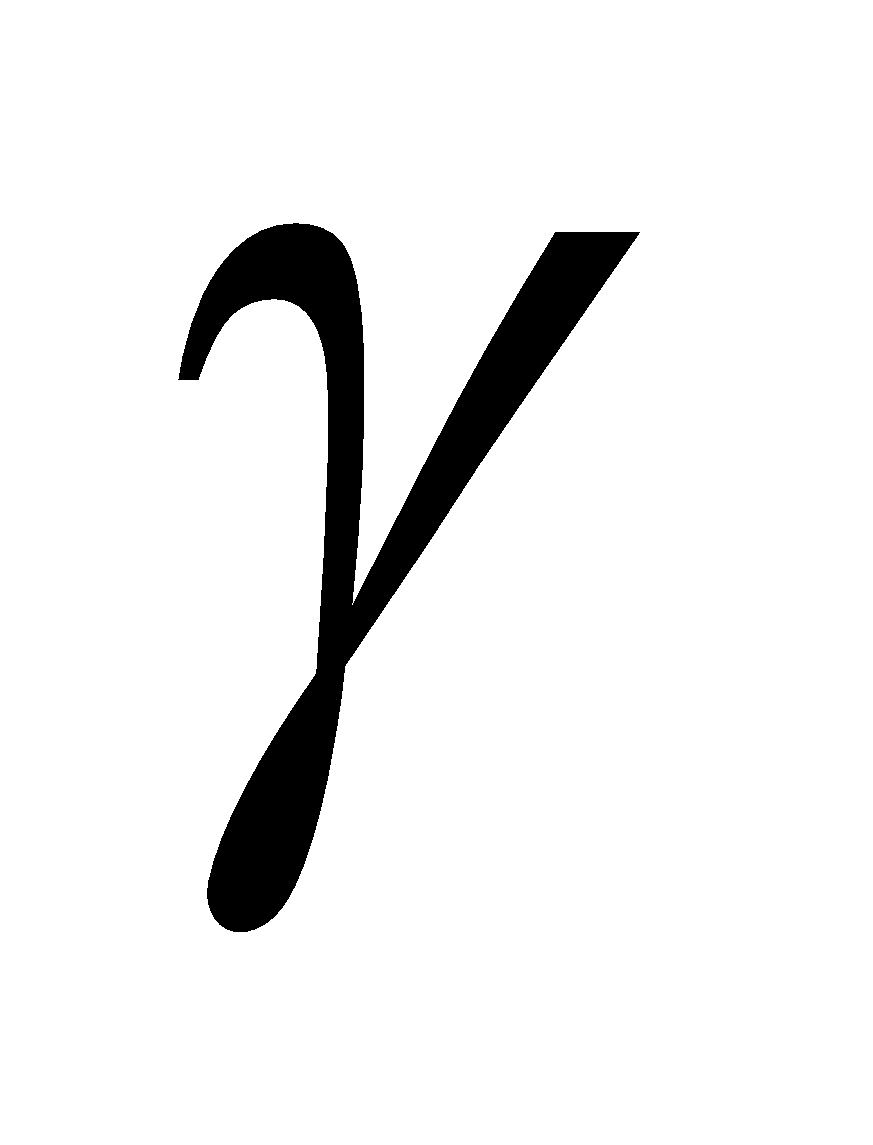 etc. The carbon atom adjacent to carboxyl group is assigned the letter
etc. The carbon atom adjacent to carboxyl group is assigned the letter  , the next
, the next  and so on
and so on
Derived System
Acids are regarded as alkyl derivatives of acetic acid eg.
IUPAC System
They are named as Alkanoic acids eg.
They are named as Alkanoic acids eg.
HCOOH Methanoic acid
C3H7COOH Butanoic acid
While naming the complex acids, the longest chain is picked up and the carbon atoms are numbered starting from carboxyl group which is given number 1.
ISOMERISM
POSITION AND CHAIN ISOMERISM
eg. C6H12O2 represent
eg. C6H12O2 represent
FUNCTIONAL ISOMERISM
GENERAL METHODS OF PREPARATION
- Oxidation of 1º alcohols and aldehydes with acid K2Cr2O7 or KMnO4
- Oxidation of methyl ketones (Haloform reaction) with X2/NaOH
- Hydrolysis of cyanides : Hydrolysis may be affected by acid or alkali
- Hydrolysis of an ester: with alkali or acid
Ease of hydrolysis 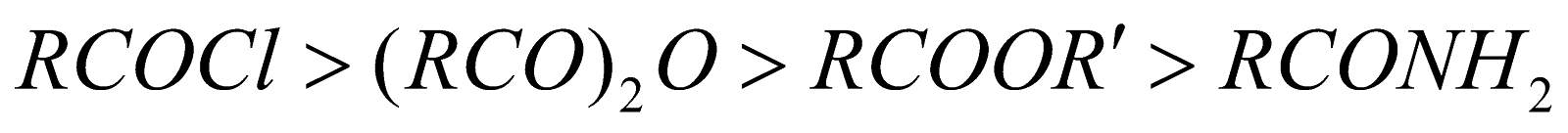
Alkaline hydrolysis of an ester is known as saponification
- Hydrolysis of trihalogen derivative of alkanes
- Carboxylation of alkenes (Koch reaction)
- Reaction of Grignard Reagents with CO2
- By heating sodium alkoxide with CO
- From Sodium alkyl and CO2
- Catalytic oxidation of long chain hydrocarbons
- From alkynes
- By heating dicarboxylic acids eg oxalic acid or malonic acid
- By acidic hydrolysis of Malonic or aceto acetic ester
MANUFACTURE OF METHANOIC ACID
MANUFACTURE OF ACETIC ACID
- By air oxidation of Acetaldehyde
- By air oxidation of Butane
- Quick vinegar process
The production is limited to the production of vinegar only which is 5 to 7% acetic acid
Glacial acetic acid
Pure acetic acid when cooled forms ice like solid (glacier) hence it is called glacial acetic acid.
GENERAL PROPERTIES
Acids upto C10 are liquids with unpleasant odours. The higher members are colourless waxy solids. Boiling points of acids increase regularly with molecular weight and higher than alcohols (of comparable molecular mass) due to formation of dimer through H-bonding
SOLUBILITY
Acids upto C4 are completely soluble in water due to H-bonding. Solubility regularly decreases rapidly due to increase in hydrophobic character of alkyl group.
MELTING POINTS
The melting point of even number acid is always higher than the next lower and higher odd number acid (alternation effect or oscillation effect) due to effective crystal lattice being symmetrical in nature*
ACIDITY OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
The carboxylic acids on ionisation produce carboxylate ion which is stabilised by resonance
Electrons releasing alkyl groups decrease the acidity. Hence lower members are more acidic than higher members eg 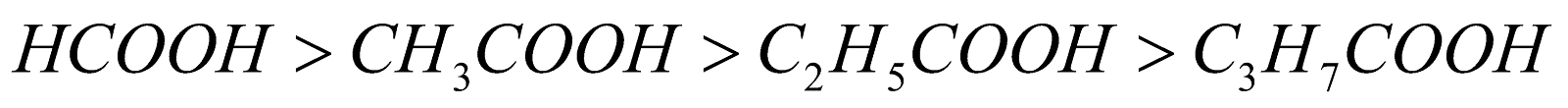
As the size of alkyl group increases the ionic character of O-H bond decreases
Electrons withdrawing substituents increase the acidity by increasing the ionic character of – O – H bond by inductive effect and dispersing the negative charge of anion formed 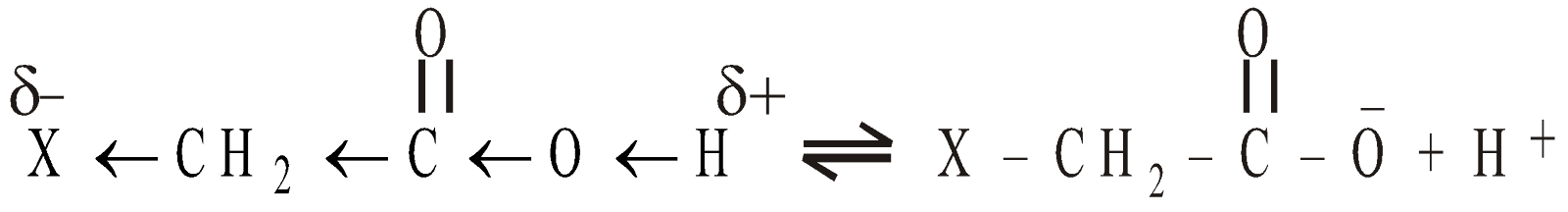
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REDUCING CHARACTER OF FORMIC ACID
ACTION OF HEAT ON FORMATES
Sodium formate 2HCOONa 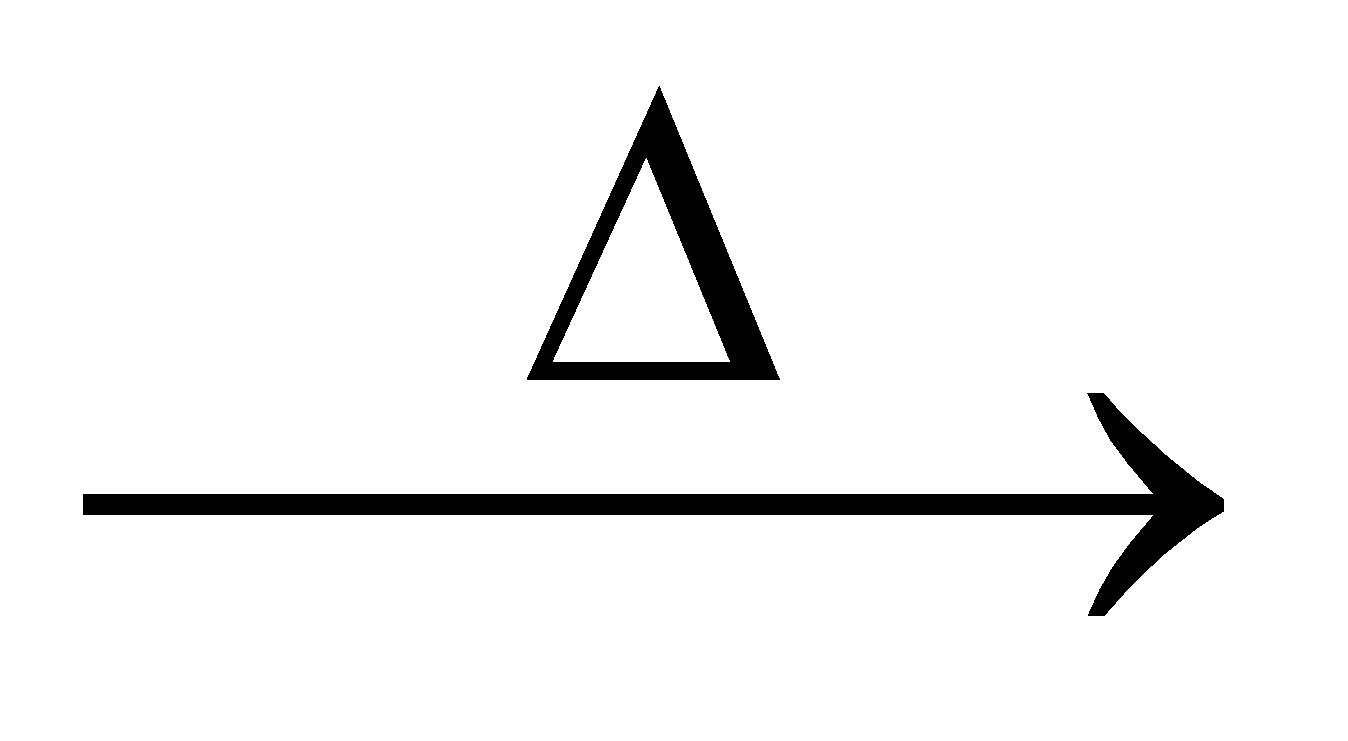 COONa + H2
COONa + H2
|
COONa
Sod. oxalate
Calcium formate 
Ammonium formate 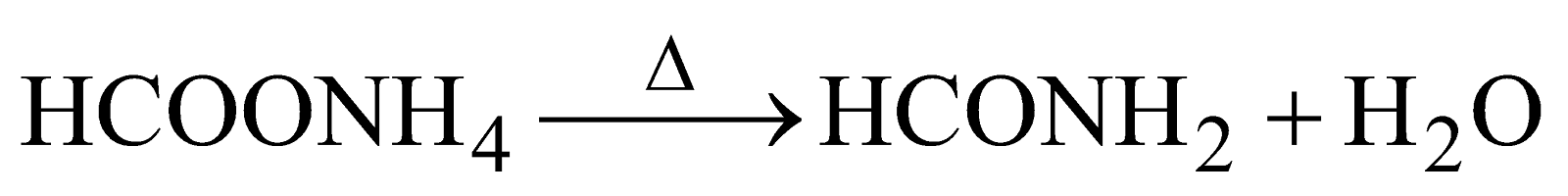
ACID DERIVATIVES
The compounds obtained by replacing –OH group of  in acid by –X, –OCOR, –OR or –NH2 are called acid derivatives. They are
in acid by –X, –OCOR, –OR or –NH2 are called acid derivatives. They are
Acid halide (X = Cl, Br, I)
Acid anhydride
Ester
Acid amide
The order of reactivity for nucleophilic substitution reactions (known as acyl substitution reactions) is as follows
The factors affecting the above order are (i) Inductive effect (ii) Resonance and (iii) Nature of leaving group. The more the basic character of the leaving group, the lesser is the reactivity and basic character follows the order
ACID CHLORIDES
IUPAC name Alkanoyl Chloride
METHODS OF PREPARATION
- From acids
- From Salts (Industrial method)
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Acid Chlorides are polar in nature, still insoluble in water due to absence of hydrogen bonding which is also the reason of their having low b.p. than acids.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
USES
- As acylating agent
- Determination of –NH2 and OH group in a molecule
ACID ANHYDRIDE (RCO)2O
IUPAC name Alkanoic anhydride
Formula Common name IUPAC name
METHODS OF PREPARATION
(mixed anhydride)
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
The anhydrides are colourless liquids with irritating smell.
Insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
USES
Acetic anhydride is used as acetylating agent in the manufacture of plastics, cellulose acetate and polyvinyl acetate.
ESTERS
IUPAC name alkyl alkanoate
Formula Common name IUPAC name
METHODS OF PREPARATION
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Esters are pleasant smelling liquids sparingly soluble in water soluble in alcohol and ether.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Note. Alcoholysis is usually effective in replacing a higher alcohol by lower one eg.
Hydrolysis of carboxylic esters may be formulated in two ways
Claisen condensation: Intermolecular condensation of esters containing a-hydrogen atom in presence of strong base to form b-keto ester
USES OF ESTERS
In making artificial essences and flavours.
AMIDES
IUPAC name Alkanamide
Formula Common name IUPAC name
HCONH2 Formamide Methanamide
CH3CONH2 Acetamide Ethanamide
METHODS OF PREPARATION
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Except formamide, amides are colourless, crystalline solids, lower members are soluble in water and alcohol. Their m.p.are higher due to hydrogen bonding
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
USES
In leather tanning and paper industry, preparation of nitrogen compounds.
UREA, CARBAMIDE (H2N.CO.NH2)
It is diamide of carbonic acid 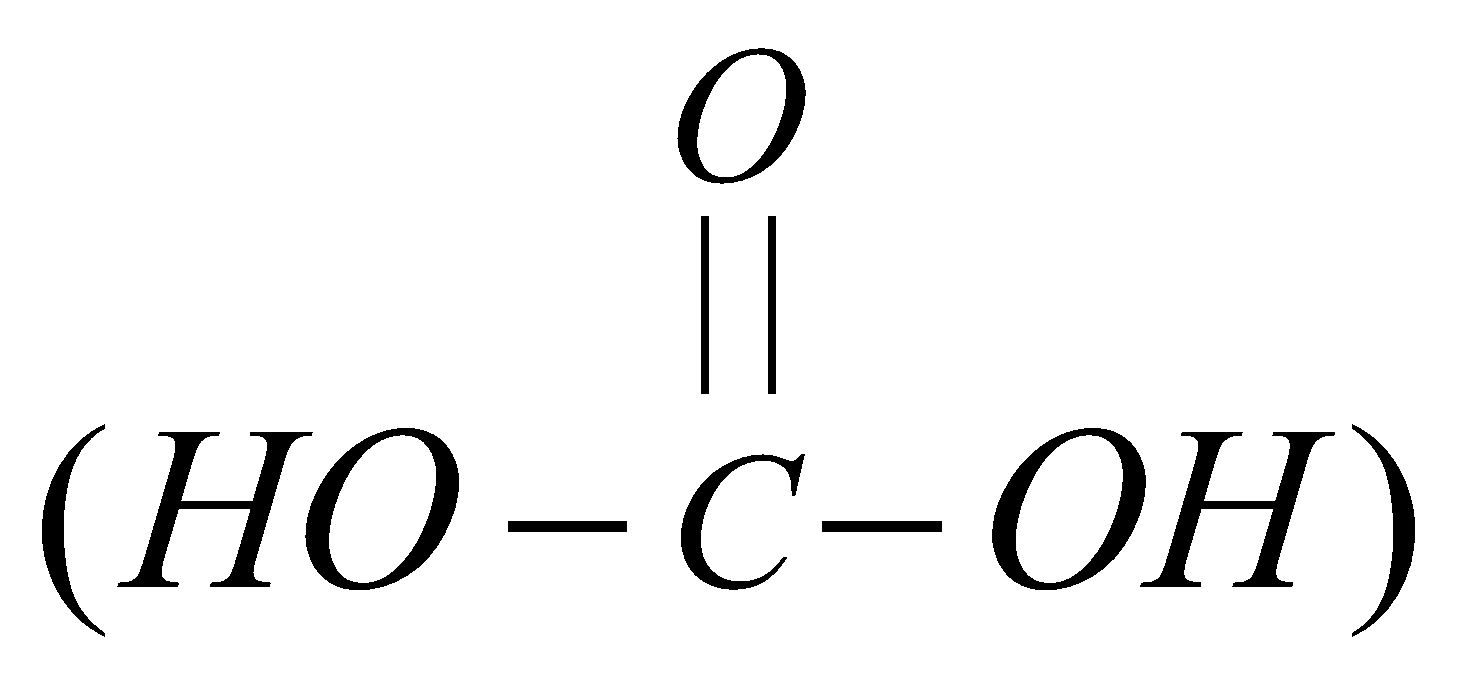
Urea is the normal end product of protein metabolism and excreted in urine about 30 gm in 24 hours by an adult person.
PREPARATION
- Wohler synthesised in 1828, urea the first organic compound by heating ammonium cyanate
- By the action of ammonia on phosgene, ethyl carbonate, chloroformate or Urethanes.
- Manufacture
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
White crystalline solid mpt 132ºC soluble in water, alcohol, insoluble in ether.
It is mono acidic base.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
USES
- It is used as fertilizer
- making barbiturates
- urea formaldehyde resin
- To improve octane number
- Stabilizer for explosives
SUBSTITUTED ACIDS
The acids obtained by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms from the alkyl group of the acid by groups such as Cl, OH, CN, NH2 etc are known as substituted acids. The position of the latter is indicated by Greek letters like a, b, g, d etc (common system) or by numbers like 1, 2, 3 etc (IUPAC System) eg.
3 - hydroxy butanoic acid (IUPAC)
Distinction between different substituted acids can be made by the application of heat
They yield 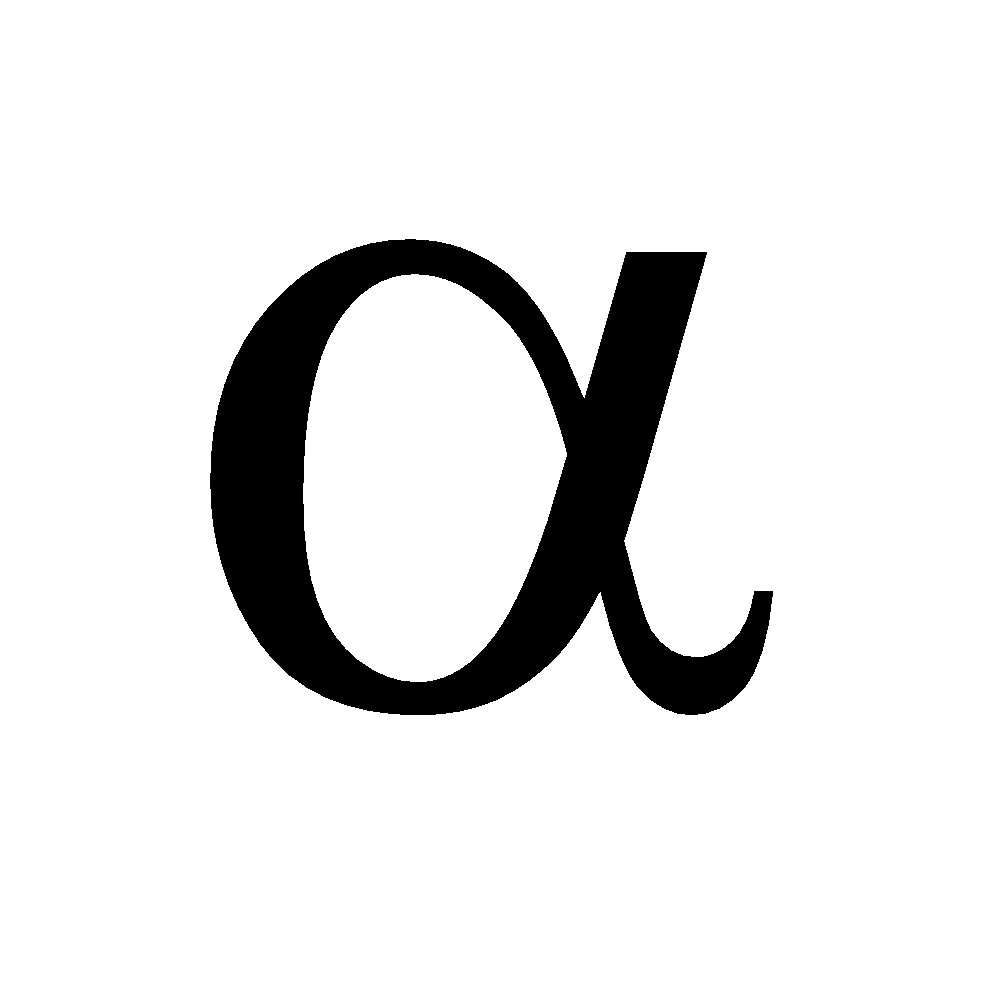 -hydroxy acids
-hydroxy acids
SATURATED DICARBOXYLIC ACIDS
The compounds containing two carboxyl groups are known as dicarboxylic acids. They have the general formula CnH2n (COOH)2
NOMENCLATURE
Their IUPAC group name is Alkanedioic acid
GENERAL PROPERTIES
- All are colourless crystalline solids, soluble in water. Solubility with increase in molecular weight, the odd acids are more soluble than even due to lower symmetry and poor packing.
- Their melting points follow the Oscillation or alternation rule which states that the melting point of an “even” acid is higher than that of the “odd” acid immediately below and above it in the series. It is also known as “saw-tooth” rule.
- Acid Strength: The strength of acids decreases from lower to higher member of the series as shown by the pka values
Acid Oxalic acid Malonic acid Succinic acid Glutaricacid Adipic acid
pka 1.271 2.86 4.21 4.34 4.41
This is due to –I effect of the carboxylic group which decreases with the length of the carbon atom chain.
- Action of heat
Blanc’s rule: On heating the acid with acetic anhydride and then distilling the product at 300ºC, 1, 4 and 1, 5 - dicarboxylic acid give cyclic anhydrides and 1, 6 and 1, 7-dicarboxylic acid give cyclic ketones provided the acids are unsubstituted. If no change the acid is 1, 8 or more.
The rule helps to determine the size of rings.
Note A 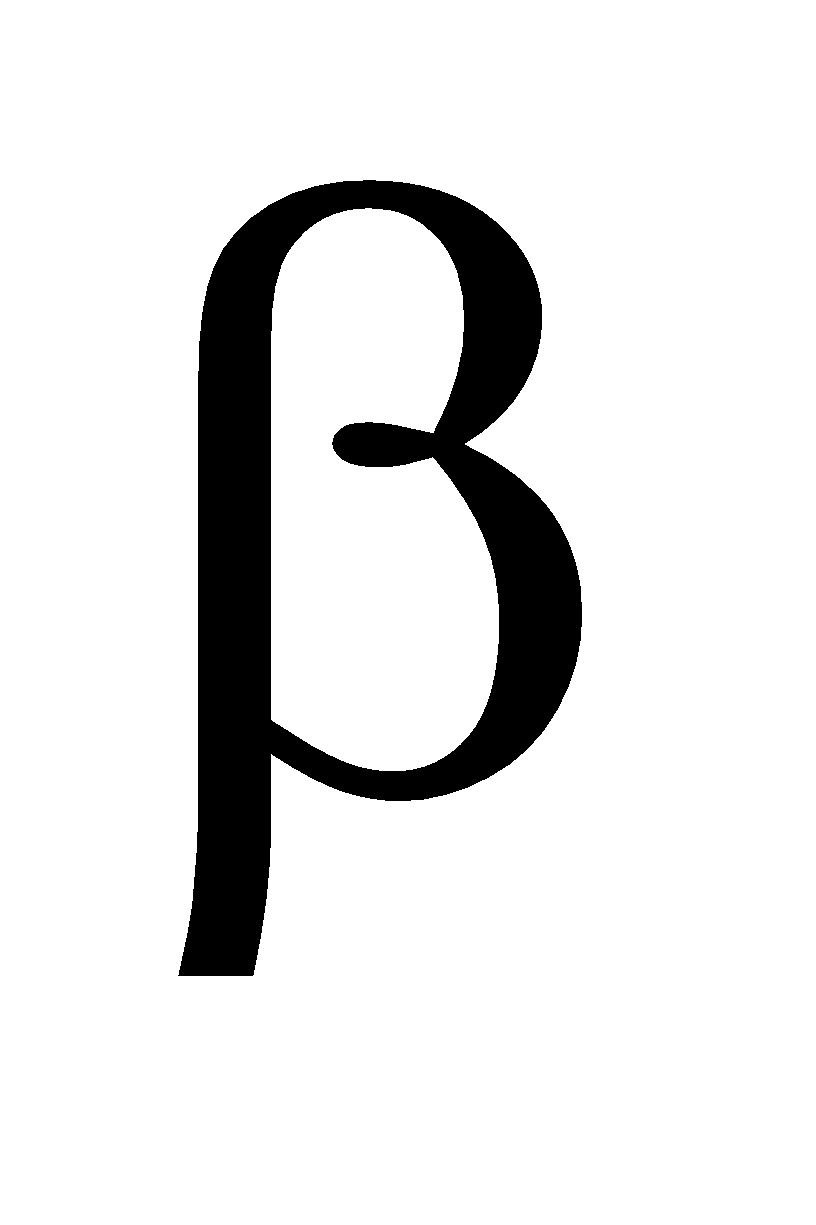 -keto acid is easily decarboxylated by heating
-keto acid is easily decarboxylated by heating
TARTARIC ACID
It occurs in free state in tamarind and as potassium salt in various fruits such as grapes, plums, etc.
PREPARATION
- From Argol or Tartar - A brown coloured crystalline mass formed during the fermentation of grape juice known as argol is crystallised from hot water to get cream of tartar which contains impure (+) potassium hydrogen tartrate. Tartaric acid is obtained as follows :
- From Glyoxal
- From Fumaric acid
- From Maleic acid
- From dibromosuccinic acid
PROPERTIES
It is colourless crystalline solid m.p. 171ºC soluble in water, alcohol, insoluble in ether. Natural tartaric acid is d-tartaric acid.
USES
- It is used in silvering mirror
- Tartar emetic is used to cause nausea and vomiting in case of poisoning
- Pot. acid tartrate is used in Baking powder
- Rochelle salt is used in preparing Fehling solution.
CITRIC ACID
It occurs in free state in citrus fruits eg.: lemon, orange lime etc. Lemon juice contains about 7% citric acid.
PREPARATION
- From lemon juice
- From Sugar - Fermentation of molasses in presence of aspergillus niger or citromyces pfeferianus and inorganic salts. eg.: (NH4)2CO3, MgSO4 etc.
- From glycerol
PROPERTIES
It is colourless crystalline substance. Its m. pt. is 100ºC soluble in water and alcohol. Insoluble in ether. Optically inactive.
Complex formation : Benedict Solution
It contain Copper Sulphate, Sodium Carbonate and Sodium Citrate. The structure of complex is
It contain Copper Sulphate, Sodium Carbonate and Sodium Citrate. The structure of complex is
It is more stable than Fehling solution
USES
- Mg Citrate is used as laxative in medicine
- As mordant in dyeing and printing
- Ferric ammonium citrate as Iron tonic
- It is used in preparing acidulated soft drinks, jams, jellies, etc.
OXALIC ACID, ETHANEDIOIC ACID (COOH)2.2H2O
PREPARATION
- Oxidation of Sucrose (Lab Method)
- Manufacture
- Hydrolysis of Cyanogen
PROPERTIES
Colourless crystalline compound. Soluble in water & alcohol, insoluble in ether m.p. 101.2ºC (hydrated) & 189.5ºC (anhydrous)
USES
- As a mordant in dyeing
- Volumetric analysis
- Removing ink stains
- In photography
BENZOIC ACID
C6H5COOH
PREPARATION
- By oxidation of alcohol or aldehyde
- By Oxidation of homologues of benzene : Oxidising agents dil. HNO3, alk. KMnO4, K2Cr2O7 + H2SO4
- By use of Grignard’s reagent
- Hydrolysis of Cyanides
- Manufacture of benzoic acid
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
It is colourless crystalline compound. Stronger than aliphatic acids and sparingly soluble in water.
Acid Character : Ortho, para directing groups with activation decrease the acid character, while meta directing groups increase the acid character of benzoic acid.
Ortho effect : Ortho substituted benzoic acids are more stronger than benzoic acid regardless of the nature of the substituent Ka of benzoic acid is 6.3 × 10–5
Acidity constants of substituted benzoic acids and order of acid strength (Ka = X × 10–5)
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
USES
Sodium benzoate is used as food preservative.
SALICYCLIC ACID
o-hydroxy benzoic acid
PREPARATION
- Kolbe-Schmidt reaction
- Reimer-Tiemann Reaction
PROPERTIES
Colourless crystalline substance m. pt. 429 K. Sublimes on heating.










