JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus can be referred by the IIT aspirants to get
a detailed list of all topics that are important in cracking the entrance
examination. JEE Advanced syllabus for Physics has been designed in such a
way that it offers very practical and application-based learning to
further make it easier for students to understand every concept or topic
by correlating it with day-to-day experiences. In comparison to the other
two subjects, the syllabus of JEE Advanced for physics is developed in
such a way so as to test the deep understanding and application of
concepts.
Gravitation is an easy to understand and a highly scoring topic. It
might have a 1% weightage in the entire JEE Physics portion but do not
neglect. You can practice these questions on regular basis to know what
are the important points to remember at the moment when
gravitation question comes.
Q1.The gravitational potential due to earth at infinite
distance from it is zero. Let the gravitational potential at a
point P be -5 J kg-1. Suppose, we arbitarily assume
the gravitational potential at infinity to be +10 J
kg-1, then the gravitational potential at P will
be
Q2.Two satellite A and B of masses m1 and m2
(m1=2 m2) are moving in circular orbits
of radii r1 and r2
(r1=4r2), respectively, around the
earth. If their periods are TA and TB,
then the ratio TA/TB is
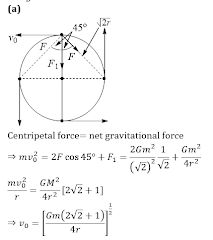
Q3.Four similar particles of mass m are orbiting in a circle
of radius r in the same angular direction because of their
mutual gravitational attractive force. Velocity of a particle
is given by
Q4.A spherically symmetric gravitational system of particles has a mass density
ρ={(ρ0 for r≤R
{0 for r>R
{0 for r>R
where ρ0 is a constant. A test mass can
undergo circular motion under the influence of the
gravitational field of particles. Its speed v as a function of
distance r(0 <r < ∞) from the centre of the system is
represented by
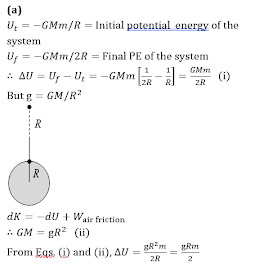
Q5.If g is the acceleration due to gravity on the earth's
surface, the gain in the potential energy of an object of mass
m raised from the surface of the earth to a height equal to
the radius R of the earth is
Q6.A satellite of mass m is orbitiing around the earth at a
height h above the surface of the earth. Mass of the earth is
M and its radius is R. The angular momentum of the satellite
is independent of
Q7.A ring having non-uniform distribution of mass M and
radius R is being considered. A point mass m0 is taken slowly
towards the ring. In doing so, work done by the external force
against the gravitational force exerted by ring is
Q8.Four particles, each of mass M, move along a circle of
radius R under the action of their mutual gravitational
attraction. The speed of each particle is
Q9.Two concentric shells of masses M1 and M2 are having
radii r1 and r2. Which of the following is the correct
expression for the gravitational filed on a mass m?
Q10.Gravitational acceleration on the surface of a planet is
√6/11 g, where g is the gravitational acceleration on the
surface of earth. The average mass density of the planet is
2/( 3) times that of the earth. If the escape speed on the
surface of the earth is taken on be 11 kms-1, the
escape speed on the surface of the planet in kms-1
will be